X-bar Chart
They are a standardized chart for variables data and help determine if a particular process is predictable and stable.
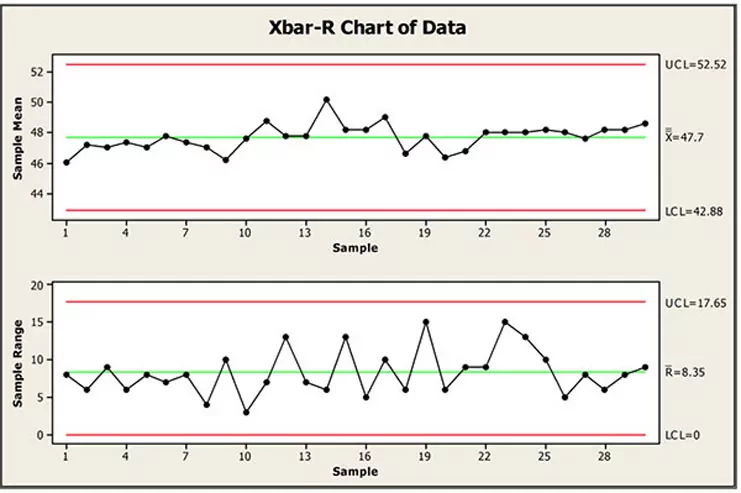
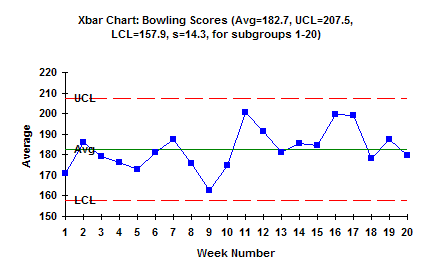
X-bar chart. X A 2 R displaystyle bar xpm A_ 2 bar R Plotted statistic. This Statistical Process Control Chart x bar and r chart example describes an effective way to create a high-level performance tracking system that includes a process capability report-out in one report-out. In total 50 observations were recorded.
They provide continuous data to determine how well a process functions and stays within acceptable levels of variation. An x-bar R chart can find the process mean x-bar and process range R over time. X Bar Chart Calculations.
In industrial statistics the X-bar chart is a type of Shewhart control chart that is used to monitor the arithmetic means of successive samples of constant size n. Some notes to keep in mind when creating an x-bar R chart include. This type of control chart is used for characteristics that can be measured on a continuous scale such as weight temperature thickness etc.
X i 1 m j 1 n x i j m n displaystyle bar x frac sum _ i1 msum _ j1 nx_ ij mn Control limits. The data must be continuous. These are used to monitor the effects of process improvement theories.
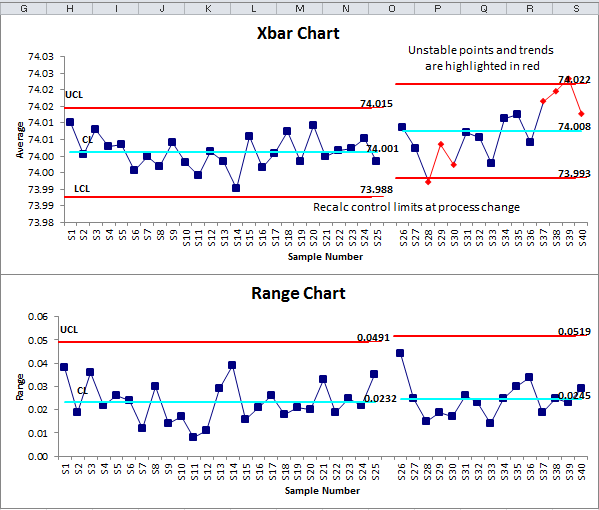
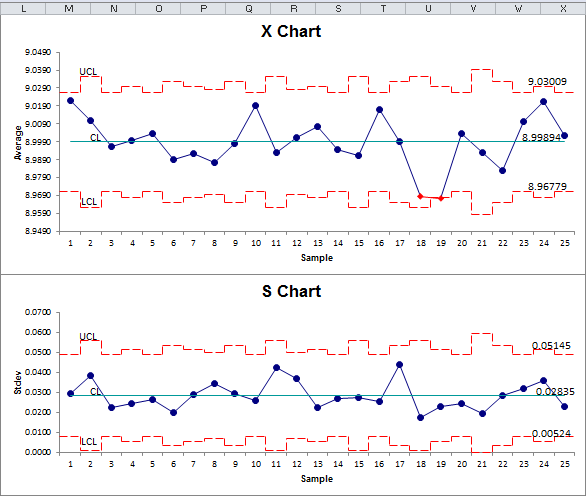
The mean or average change in process over time from subgroup values. The control limits here were calculated including subgroups 21 to 25 which have a known assignable cause. The range of the process over the time from subgroups values.
Some authors prefer to write this x-bar chart formula as. The X-bar chart measures between-sample variation signal while the R chart measures within-sample variation noise. Select Shots 1-3 click Numeric Data Variables Y.
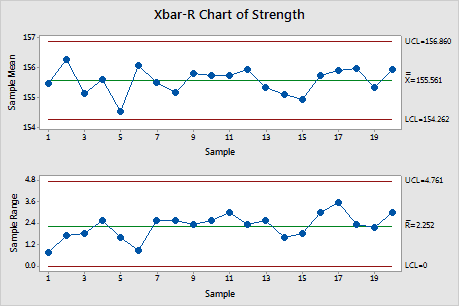
The Xbar chart below shows an out of control process. The mean or average change in process over time from subgroup values. The Xbar R chart is the most commonly used control chart.
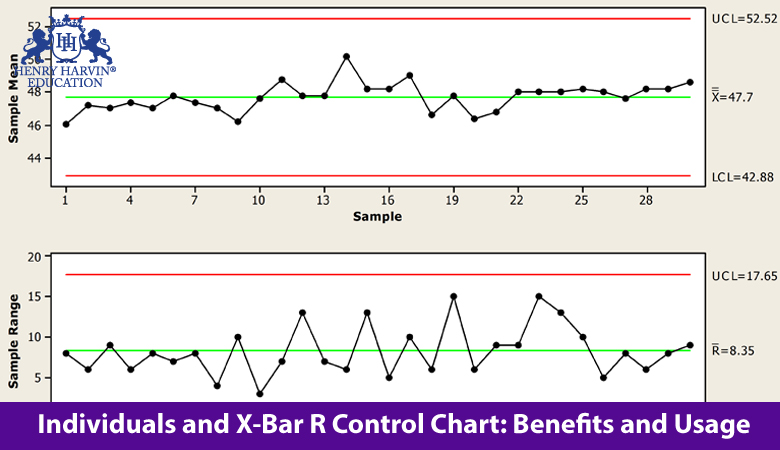
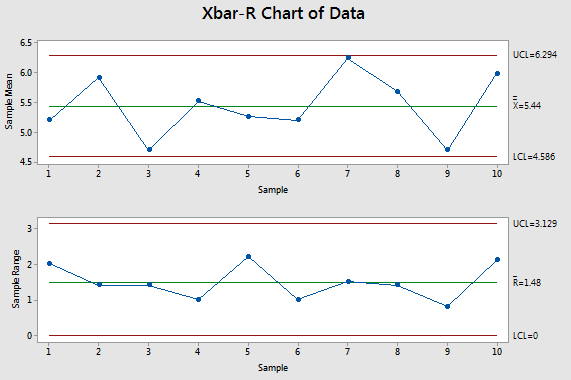
An X-Bar and R-Chart are control charts utilized with processes that have subgroup sizes of 2 or more. Each data point is the mean of a subgroup of 5 observations. Here is some further information about the charts.
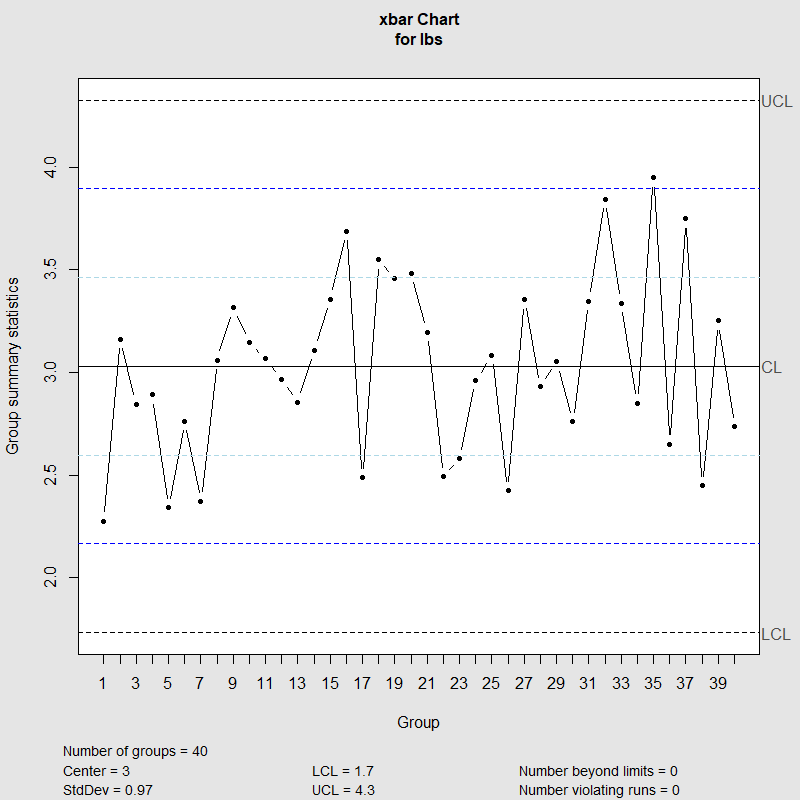
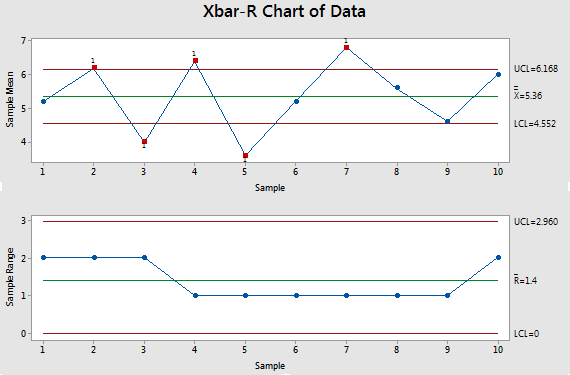
Engineers must take a special look at these points in order to identify and assign causes. The x-bar chart generated by R provides significant information for its interpretation including the samples Number of groups control limits the overall mean Center the standard deviation StdDev and most importantly the points beyond the control limits and the violating runs. Statistical software will normally have the ability to test for conditions that indicate process control or the lack thereof.
The control limits on the X-Bar brings the samples mean and center into consideration. Check Use Entire Data Table. The control limits on the X-Bar brings the samples mean and center into consideration.
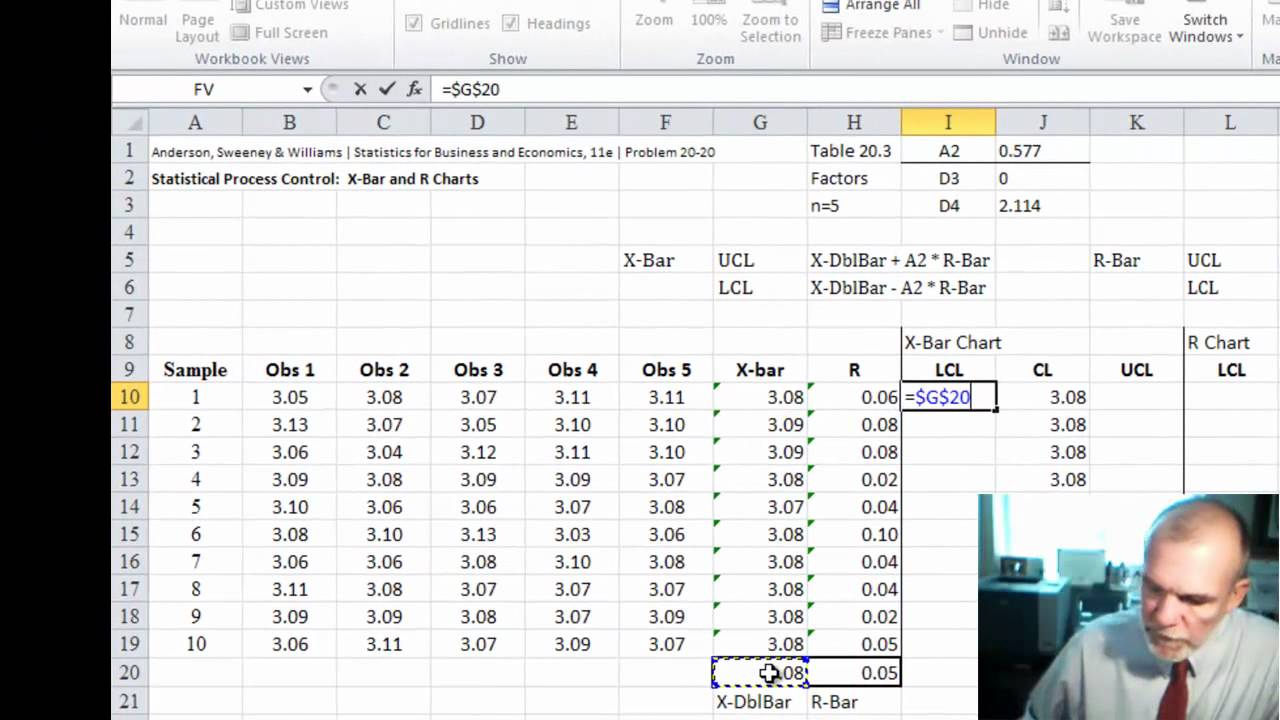
X i j 1 n x i j n displaystyle bar x_ i frac sum _ j1 nx_ ij n. Click SigmaXL Control Charts X-Bar R. X-Bar and R-Charts are typically used when the subgroup size lies between 2 and 10.
X-barR charts are a pair of control charts where continuous or variable data is collected in rational subgroups. Ensure that Calculate Limits is selected. The described 30000-foot-level reporting first assesses process stability from a high-level vantage point and then if the process is stable.
For example one might take a sample of 5 shafts from production every hour. This monitors the spread of the process over the time. X-bar Chart Limits The lower and upper control limits for the X-bar chart are calculated using the formula s n LCL x m σˆ n UCL x m σˆ where m is a multiplier usually set to 3 chosen to control the likelihood of false alarms out -of-control signals when the process is in control.
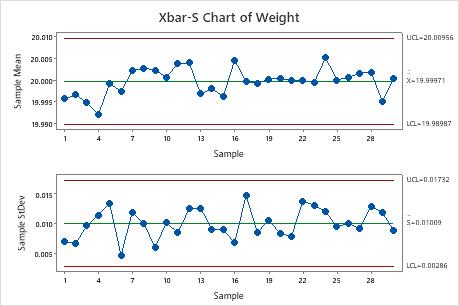
X Bar S Control Chart Definitions. 26 rows X-bar control limits are based on either range or sigma depending on which chart it. UCL LCL Upper and Lower Control Limit where x-double bar is the Grand Average and σx is Process Sigma which is calculated using the Subgroup Range or Subgroup Sigma statistic.