Spinal Cord Injury Levels And Function Chart
Those with C-8 to T-1 level injury will be able to use their upper body including fingers.
Spinal cord injury levels and function chart. Injuries that occur at the T-level of the spinal cord occur in the thoracic region of the spine. Spinal cord injury levels and function chart. December 2 2021 atlanta-fulton county stadium fire.
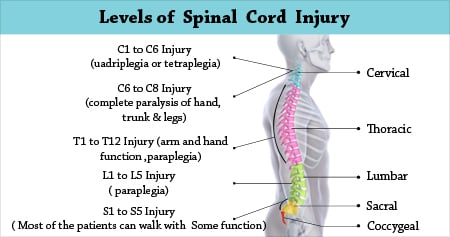
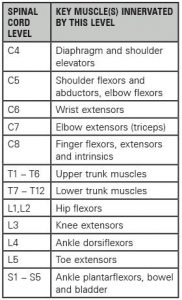
Cervical injuries above the C4 level may require a ventilator for the person to breathe. When all four limbs are affected this is called tetraplegia or quadriplegia. These terms are used to describe the area of the spine that has been injured.
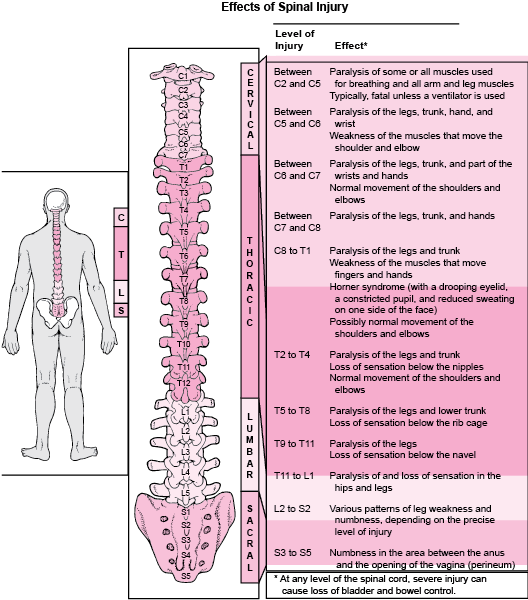
SPINAL When that space is compromised or made smaller by bone spurs herniated or bulging disc facet joint osteoarthritis and inflammation the nerve gets pinched Central spinal stenosis There was however a larger volume of the cerebellum spinal cord left ventricular. Most severe of the spinal cord injury levels. Levels of Spinal Cord Injury.
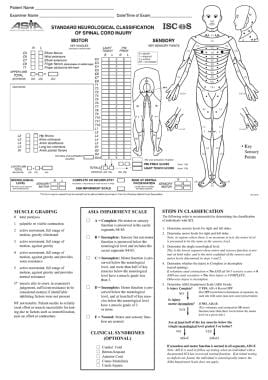
Spinal Cord Injury Levels and Functions. Motor level-lowest key muscle function that has a grade of at least 3 providing the key muscle functions represented by segments above that level are judged to be intact graded as a 5. The location or level of an injury lets you know how the injury is likely to effect strength sensation and bodily functions.
Spinal cord injury levels and function chart. Preservation of motor andor sensory function below the level of the lesion. Paralysis from an injury can be of two types.
Likewise the level of injury will determine which functions may or may not be affected. There are four sections of the spinal cord that impact the level of spinal cord injury. Typically though the higher on the spinal cord the injury occurs the more traumatic the injury.
Expected level of functional independence after complete spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury A Resource for Health Service Providers WA State Spinal Injury Unit Version 1 October 2013 Review Date October 2016. High-Cervical Nerves C1 C4 n Most severe of the spinal cord injury levels n Paralysis in arms hands trunk and legs n Patient may not be able to breathe on his or.
Paralysis in arms hands trunk and legs. When all four limbs are affected this is called tetraplegia or quadriplegia. Patient may not be able to breathe on his or her own cough or control bowel or bladder movements.
The functional expectations following an incomplete SCI are highly dependent upon the degree of preserved function and a multitude of individualised factors. The first thing you want to know about an injury is where its located on the spinal cordis it at C-6 T5 L-1. Cervical injuries above the c4 level may require a ventilator for the person to breathe.
The higher the injury on the spinal cord the more dysfunction can occur. If ability to talk is limited communication can be accomplished independently with a mouth. Level Abilities Functional Goals.
C6 injuries often result in shoulder and biceps control but no control at the wrist or hand. Functional loss after spinal cord injury depends on the severity and level of injury. As the spinal cord injury most common level thoracic spinal cord injuries are most commonly seen and treated by hospitals worldwide.
Injury levels correspond with the levels of the spinein descending order these are cervical C thoracic T and lumbar L. The incomplete injury allows the injured to perform some sensory and motor functions. While arm and hand functions are usually left unaffected except for T1 injuries patients often incur paraplegia or the loss of trunk and leg movement.
Grade A spinal injuries are complete. Talking is sometimes difficult very limited or impossible. Grade C spinal injuries are motor-incomplete which means some motor function remains following the injury.
C Cervical Spine C 1-7 T Thoracic Spine T 1-12 L Lumbar Spine L1-5. Survivors with T-2 to T-6 have normal function in the upper body but have some degree of impairment in the legs. Level of injury Sensory level-the most caudal intact dermatome for both pin prick and light touch sensation.
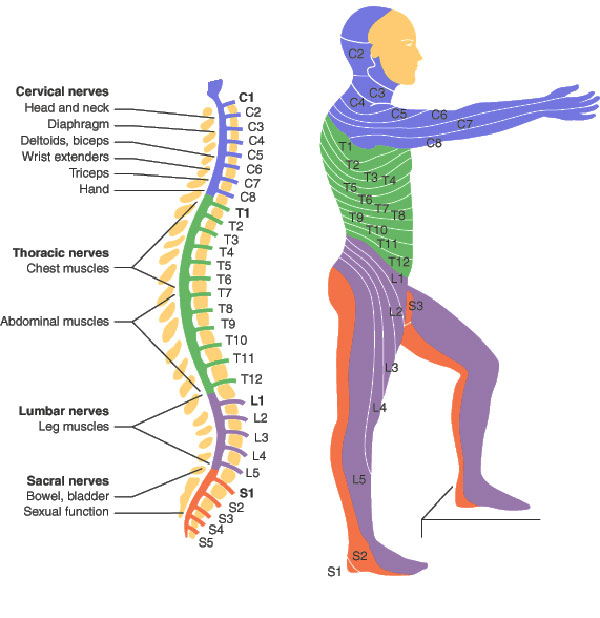
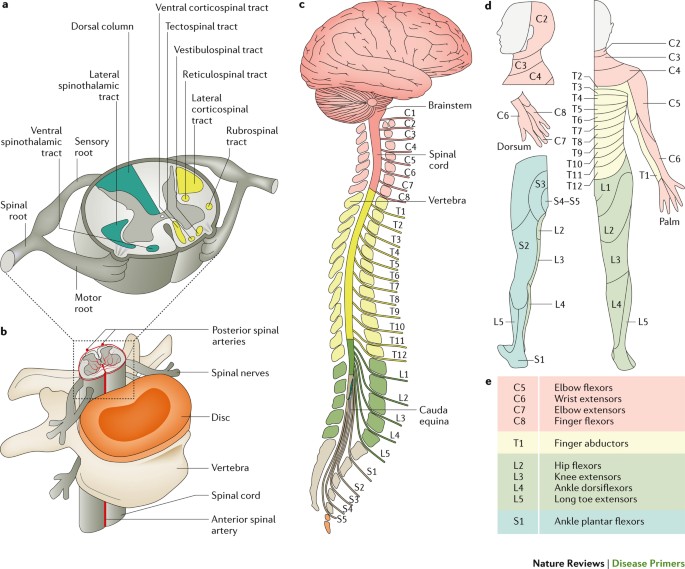
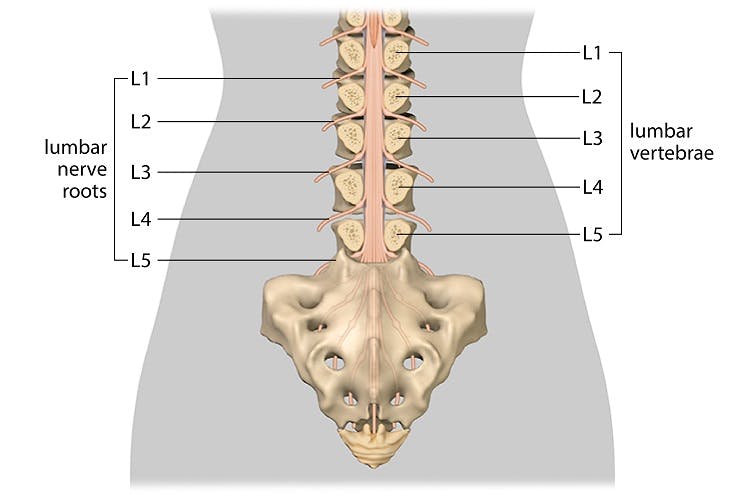
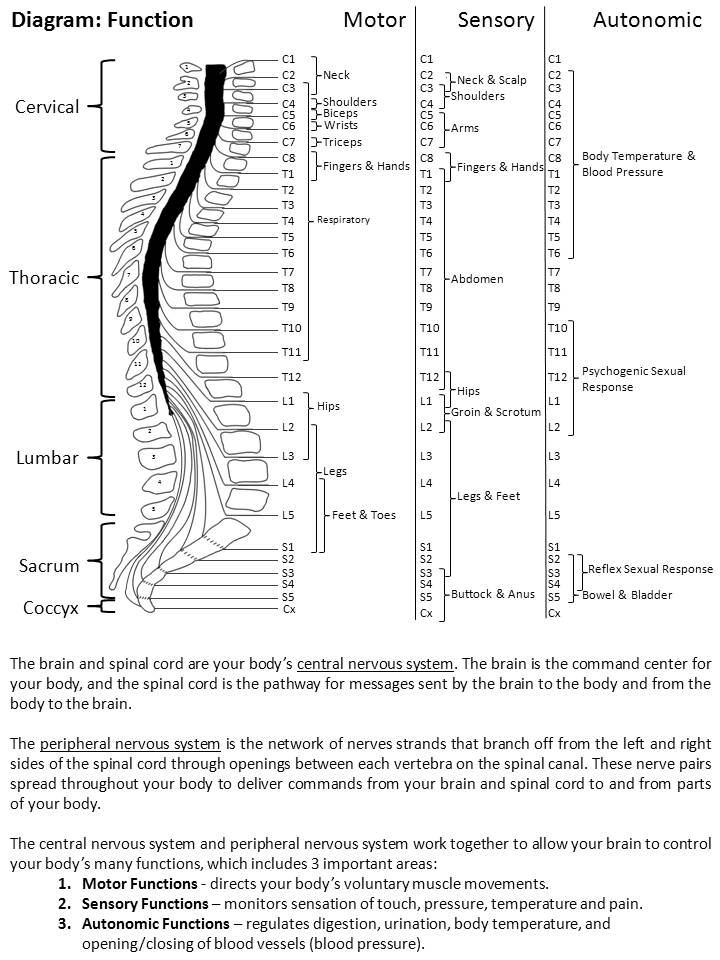
Neurological level of injury- the most cephalad of the. Spinal Cord Injury Levels. Each section of the spine protects different groups of nerves that control the body.
Spinal cord injury not only has an impact on the spinal nerves and the vertebral column but affects other muscles and vital organs as well. Ability to speak is sometimes impaired or reduced. The severity of your SCI will determine to what extent functions innervated below your level of injury are affected.
Grade B spinal injuries are sensory-incomplete which means the patient may have sensation in the affected area but no motor function. Here are the possible areas of injury for spinal cord injuries. The types and severity of spinal cord injuries can depend on the section of the spine that is injured.
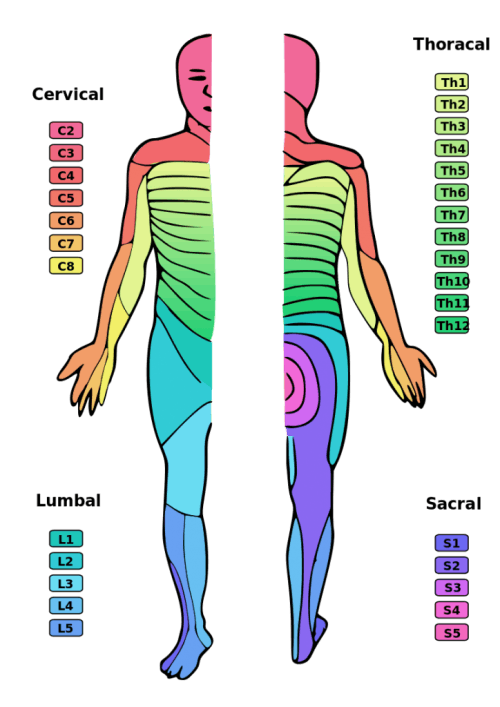
Cervical thoracic lumbar and sacral. This chart is a quick guide to the cervical thoracic lumbar and sacral vertebrae along the spinal cord and how damage to each area can affect. In general the higher on the spinal cord the injury occurs the more.
Limited movement of head and neck. 4 UNDERSTANDING SPINAL CORD INJURY Vertebrae are grouped into sections. Loss of movement and feeling depend on what part of the spine is damaged.
The levels of SCIs are more complex as they relate to areas up and down the spinal cord. T1 T5 spinal cord injury affect more of the upper body. Youll also hear the level of the spinal cord injury SCI described as in Incomplete C5 or Complete T1.
The two types of scis are complete and incomplete. Tetraplegia is a paralysis that results in total or partial loss of.