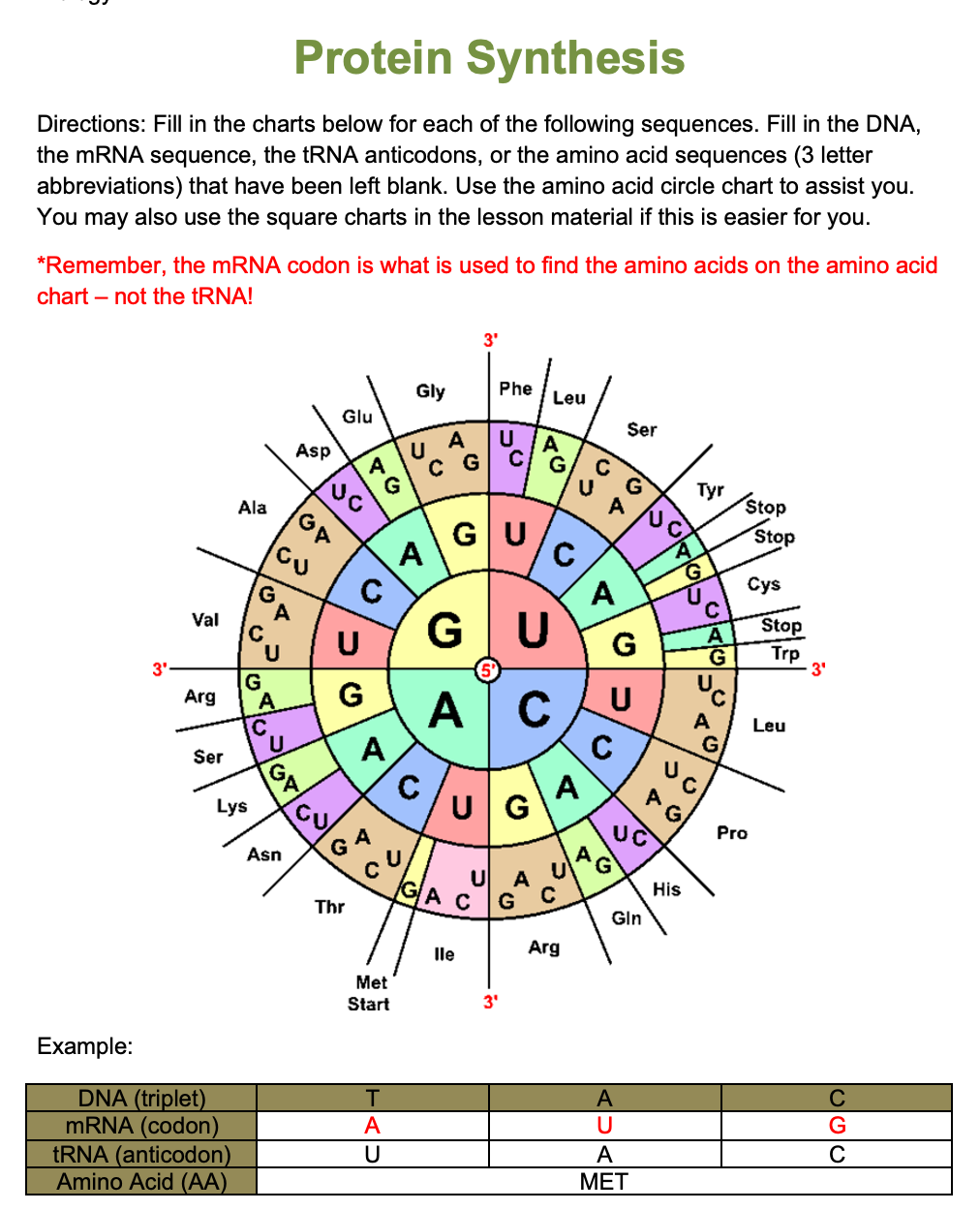
Mrna To Amino Acid Chart
In this context the standard.
Mrna to amino acid chart. Nucleotides Messenger R NR Nuclear leaues nucleus membrane LABEL 01 Ri bosomel RNA A. Translation Translation results in the synthesis of a polypeptide chain Linear chain of amino acids whose sequence is specified by the sequence of codons in mRNA Translation occurs at the ribosomes Ribosomes contain several types of ribosomal RNA rRNA and ribosomal proteins. To determine the amino acid sequence of a dna strand you must first convert it to an mRNA strand.
Fill in Step I and Step 2 choose between transcription and translation B. The A amino acid site is the location at which the aminoacyl-tRNA anticodon base pairs up with the mRNA codon ensuring that correct amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain. All of this is controlled by a ribosome - a hugely complicated structure involving protein molecules and yet another form of RNA ribosomal RNA or rRNA.
Codon charts are used to find the Amino Acid that corresponds to DNA and RNA to produce a chain of amino acids called a polypeptide or protein. Ribosome large subunit tRNA mRNA codons olypeptide amino acid polymer ribosome small. This is going to be quite complicated.
Mutation Mutation any change in the sequence of DNA Mutagen any agent causing a mutation to occur Example Radiation Three types of mutations 1. All other amino acids have more than one codon. 1 and 3 have the same amino.
A gene is a long chain of nucleotides that translates into mRNA which is a readable form. During protein synthesis an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA reads its base sequence and uses the genetic. Messenger RNA mRNA is a single-stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands of a gene.
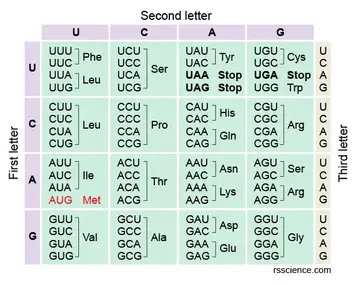
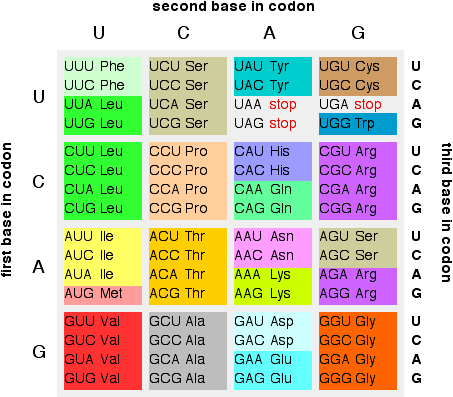
Find the second. ACC GGA TAT AGC CGA GGG TTT AAA AAA GGA CGC CGA GGT. The standard genetic code is traditionally represented as an RNA codon table because when proteins are made in a cell by ribosomes it is messenger RNA that directs protein synthesis.
Display the Mutations Identification Problems. Cells decode mRNAs by reading their nucleotides in groups of three called codons. You then go to the top of the chart and find the second.
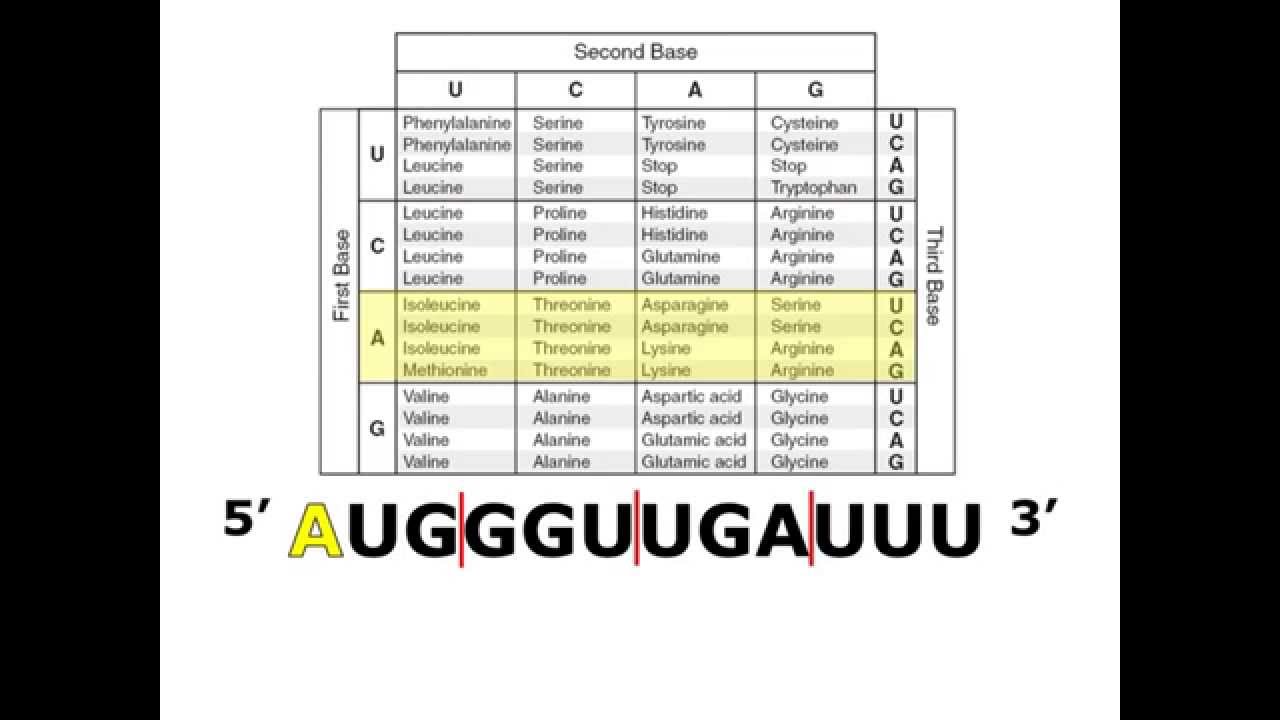
11 rows Find a codons first base in the first column of the chart. Amino a acids Step 1. So lets say that our sequence given to us is.
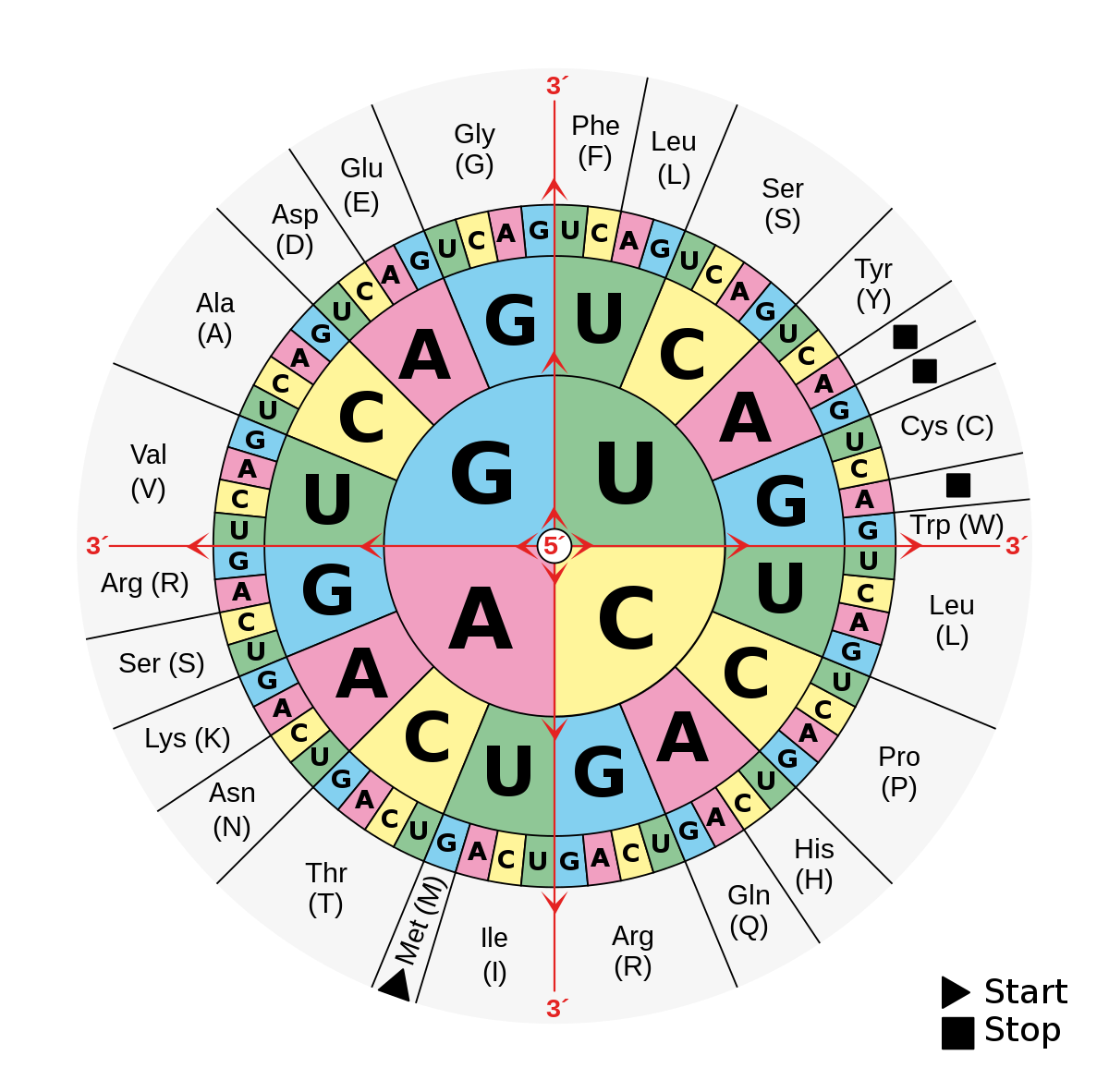
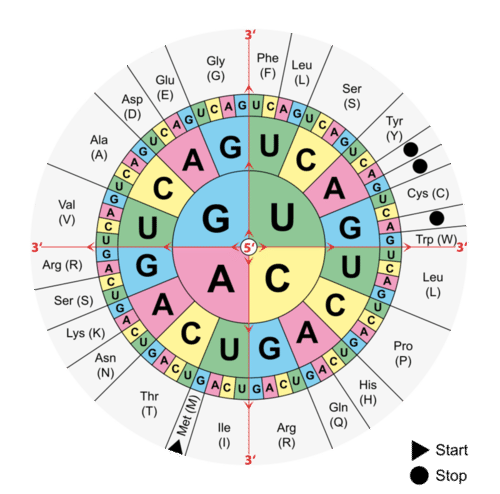
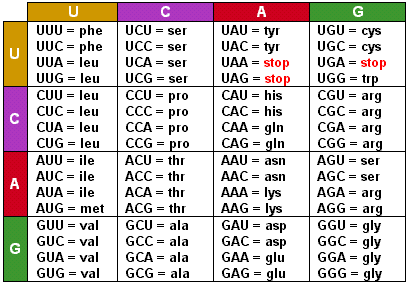
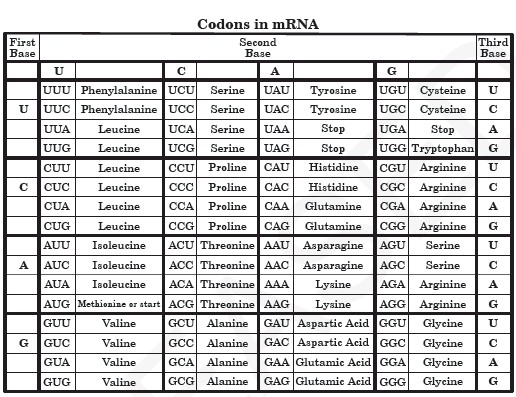
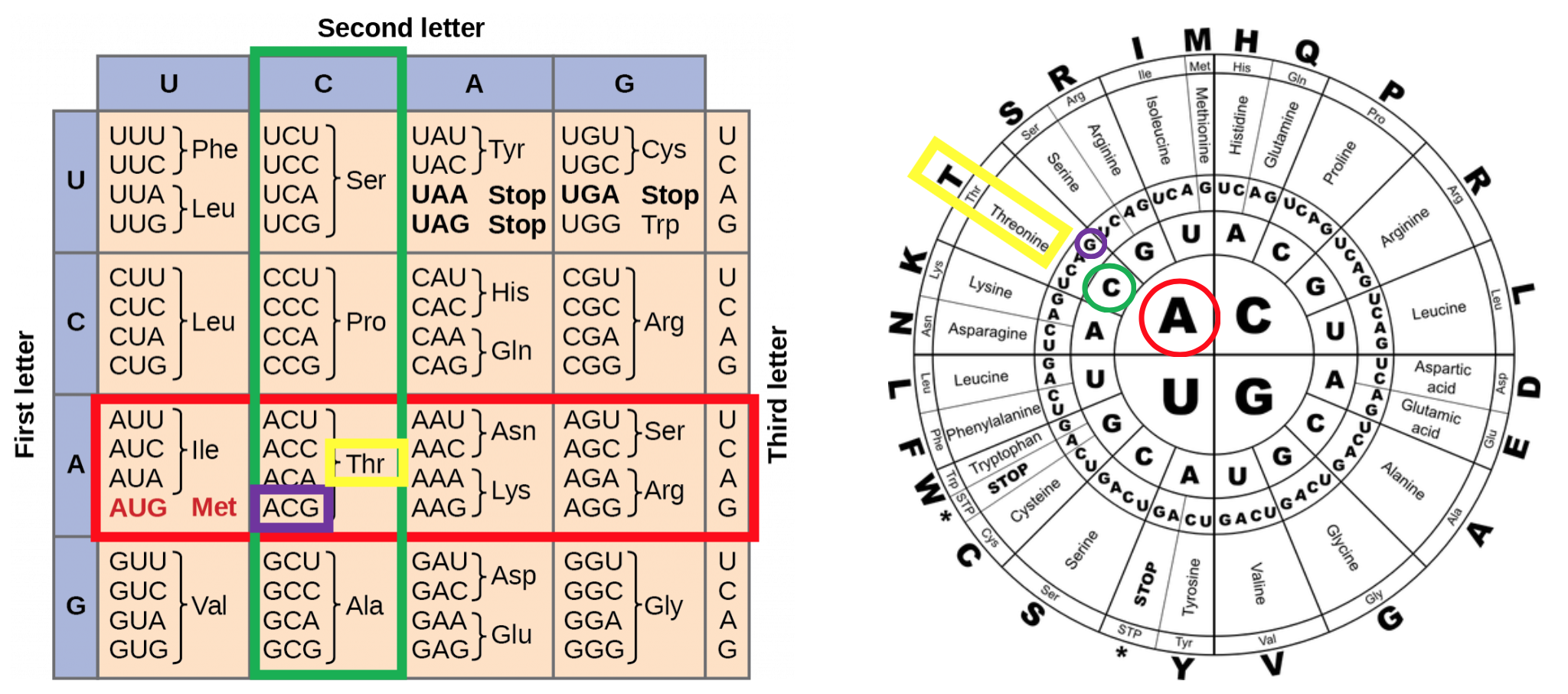
A codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. Here are some features of codons. Three stop codons mark the end of a protein.
BetterLesson reimagines professional learning by personalizing support for educators to. A genetic code is a triple nucleotide combination having information to make amino acid. DNA is changed to mRNA by transcription and and changed to amino acids by using the codon chart to identify them.
Stay in this row. Codons in an mRNA are read during translation. Fill in the appropriate number below refer to the figure.
Always use the mRNA codon it you have a DNA sequence you will have to transcribe it into an mRNA codon first. Most codons specify an amino acid. First you go to the left side of the chart and find the first letter nitrogen base of the codon.
28 rows To form a protein amino acids are polymerized with the formation of a peptide bond starting at. MUtations hTorks Original DNA Sequence T ACACCTTGGCGACGACT MRNA Sequence ATGGAACCGCTGGTGA Amino Acid Sequence U A C C UUGGCGACCACU wwww Mutated DNA Sequence 1 T A CATCITGGCGACGACT MRNA Sequence ATGAGAACCG CTGCTGA Amino Acid Sequence U A CUCUUGGCGACU What type of mutation is this. This is an example of a deletion resulting in a frame shift.
A group of three nucleotides of mRNA is a codon having information to code for an amino acid. The mRNA is an RNA version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made. TEF ATC ATE TET HER AT This sentence no longer makes sense.
Explain that students will use the mRNA and amino acid sequences to identify the mutation that occurred and the effects of each one. MRNA and position amino acids during translation. Methionine and Tryptophan have only one codon.
Impact of Mutation Need Codon Chart Original. First Base in the Codon Second Base of the Codon Third Base in the Codon U C A G U Phenylalanine. Remember that in mRNA strands A connects with U T connects with A and G connects with C C.
You must convert this to a mRNA strand. The anticodons of tRNA adapt each three-base mRNA codon to the corresponding amino acid. The mRNA sequence is determined by the sequence of genomic DNA.
Student-Centered Learning Our Content Partners. AUG GCU Amino Acid. One start codon AUG marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine.
The process of making mRNA. Resulting in a codon that encoded the same amino acid as the original amino acid. A codon chart is used to determine the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide.
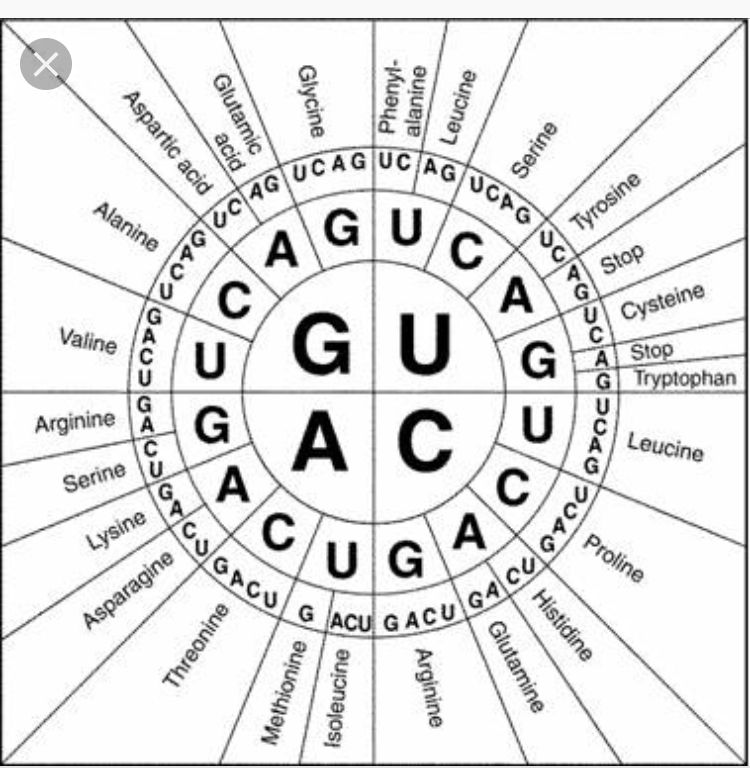
These charts allow you to use an mRNA sequence and determine the proper amino acid that corresponds to the codon. Codon Chart and Wheel. The amino acids have to be carried to the messenger RNA by another type of RNA known as transfer RNA - abbreviated to tRNA as opposed to mRNA for messenger RNA.