Hepatitis B Serology Chart
Interpretation of Hepatitis Serology.
Hepatitis b serology chart. When they find a significant concentration in your blood it shows you have a hepatitis B virus infection which may be chronic or acute. Presence indicates recent acute infection Occasionally detectable in low amount during. Brown Jr7 Natalie H.
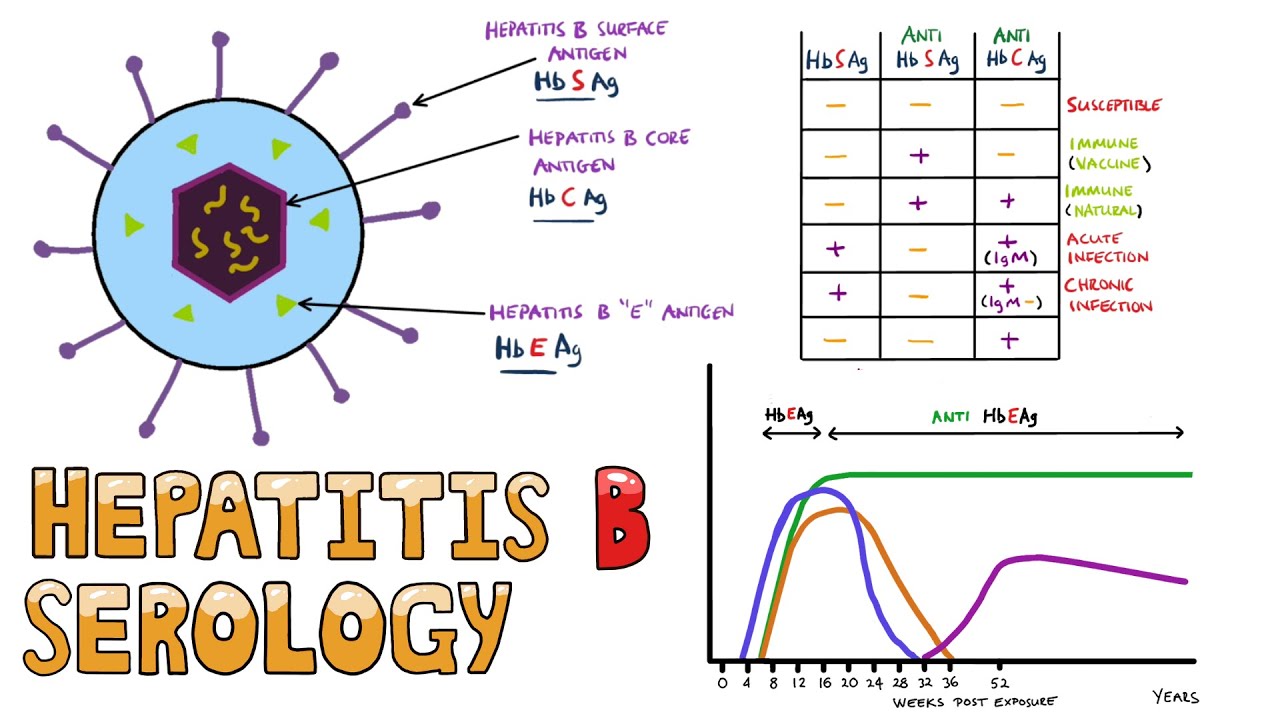
AASLD Guidelines for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Norah A. HBsAg hepatitis B surface antigen. Hepatitis B vaccine does not contain this antigen AntiHBc Develops in all those who get HBV infection whether acute or chronic Does not develop after immunization Two types IgM and IgG IgM antiHBc Appears following acute infection and persists for up to6 months Hence.
13 rows Hepatitis B Surface Antigen HBsAg Hepatitis B Surface Antibody HBsAb Hepatitis B. Most people are asymptomatic although some will present with complications such as cirrhosis hepatocellular. Viral Hepatitis Serology Training.
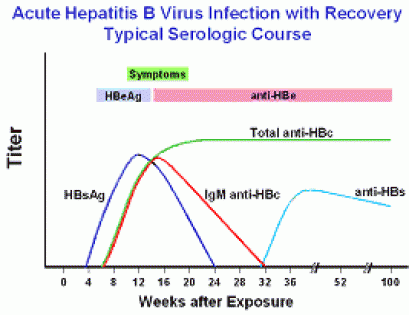
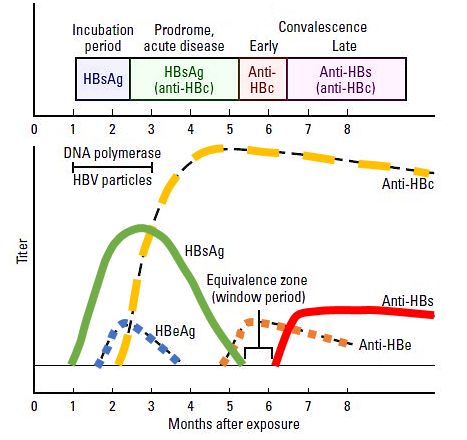
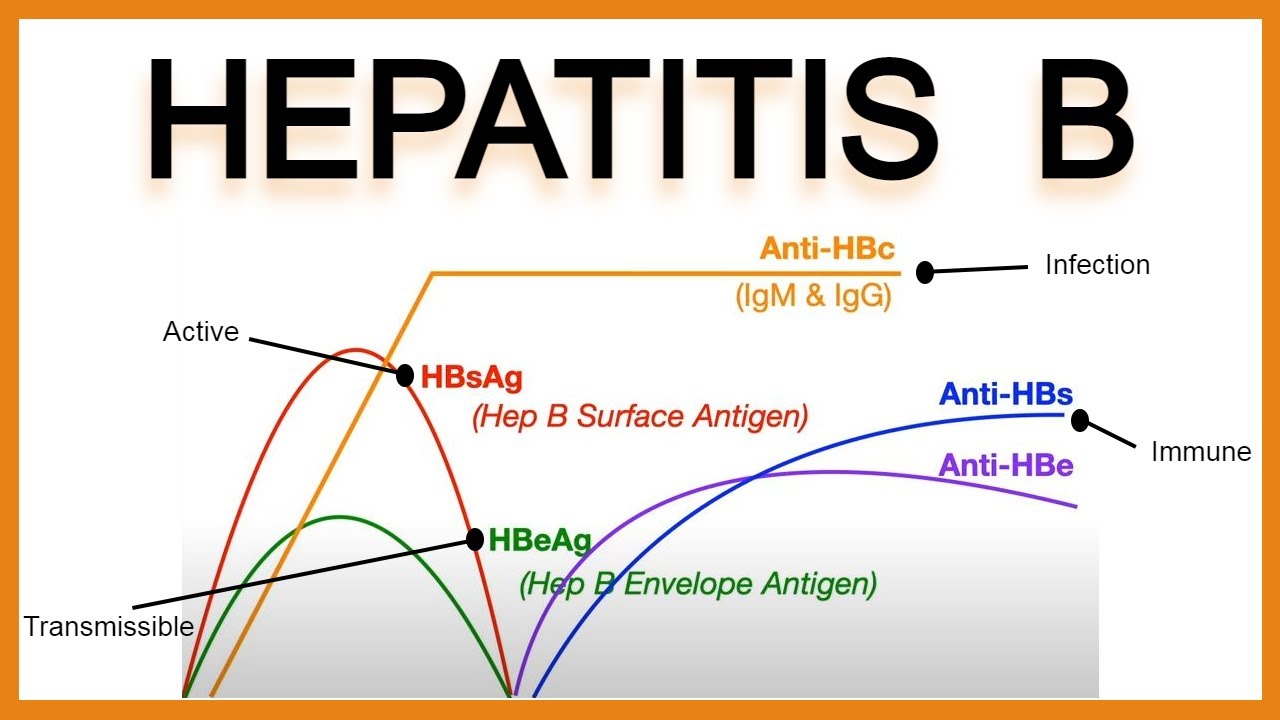
HBsAg hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker to appear in a new acute infection which can be detected as early as 1 week and as late as 9 weeks with an average of one month after exposure to the. Wong9 Purpose and Scope of the Guidance This AASLD 2018 Hepatitis B Guidance is intended to complement the AASLD. The anti-HBs antibody and anti-HBe antibody are both negative indicating he has not had spontaneous sero-conversion and he still has the hepatitis B virus.
McMahon3 Kyong-Mi Chang4 Jessica P. Indicates current or recent infection with hepatitis A. This is the test that should be ordered for a patient who is.
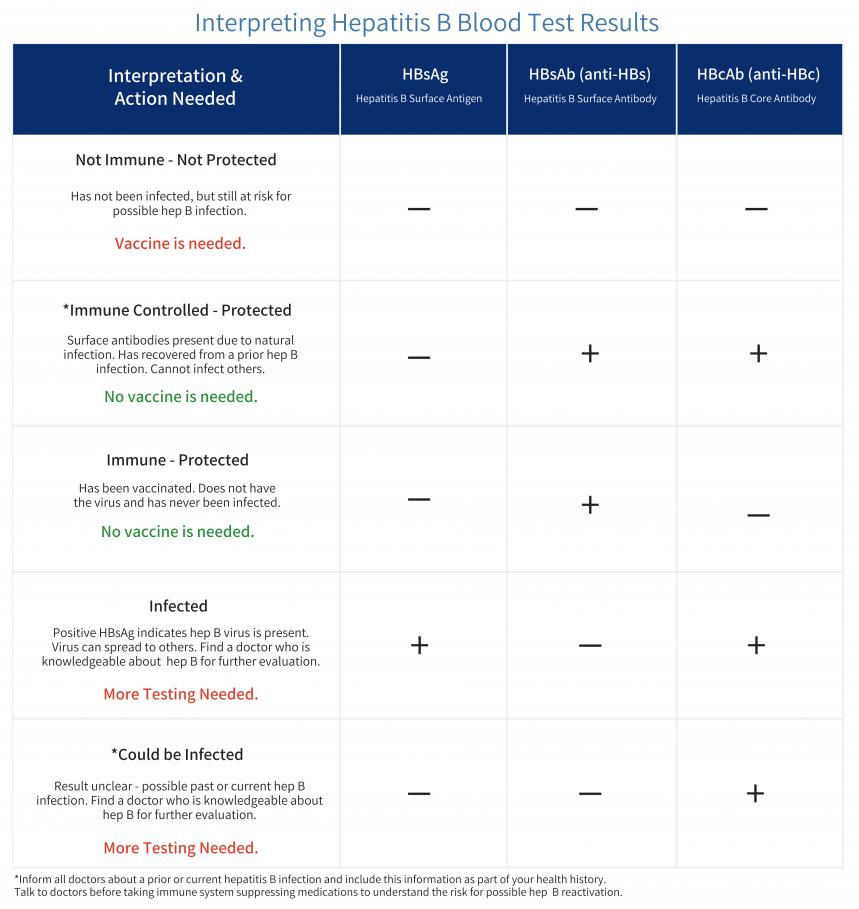
Hepatitis B infection is the most common liver infection globally caused by the hepatitis B virus HBV. According to the CDC a hepatitis B blood test result or serologic marker varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection. Tests in the Hepatitis B Serologic Panel.
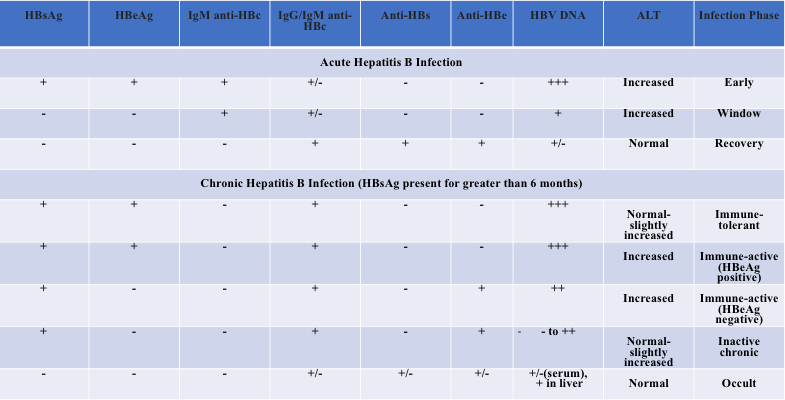
HistoryPhysical Examination Routine Laboratory Tests SerologyVirology ImagingStaging Studies All patients Symptomssigns of cirrhosis. This protein sets off your bodys immune. The results of hepatitis B serologic testing and their corresponding interpretation are shown in below.
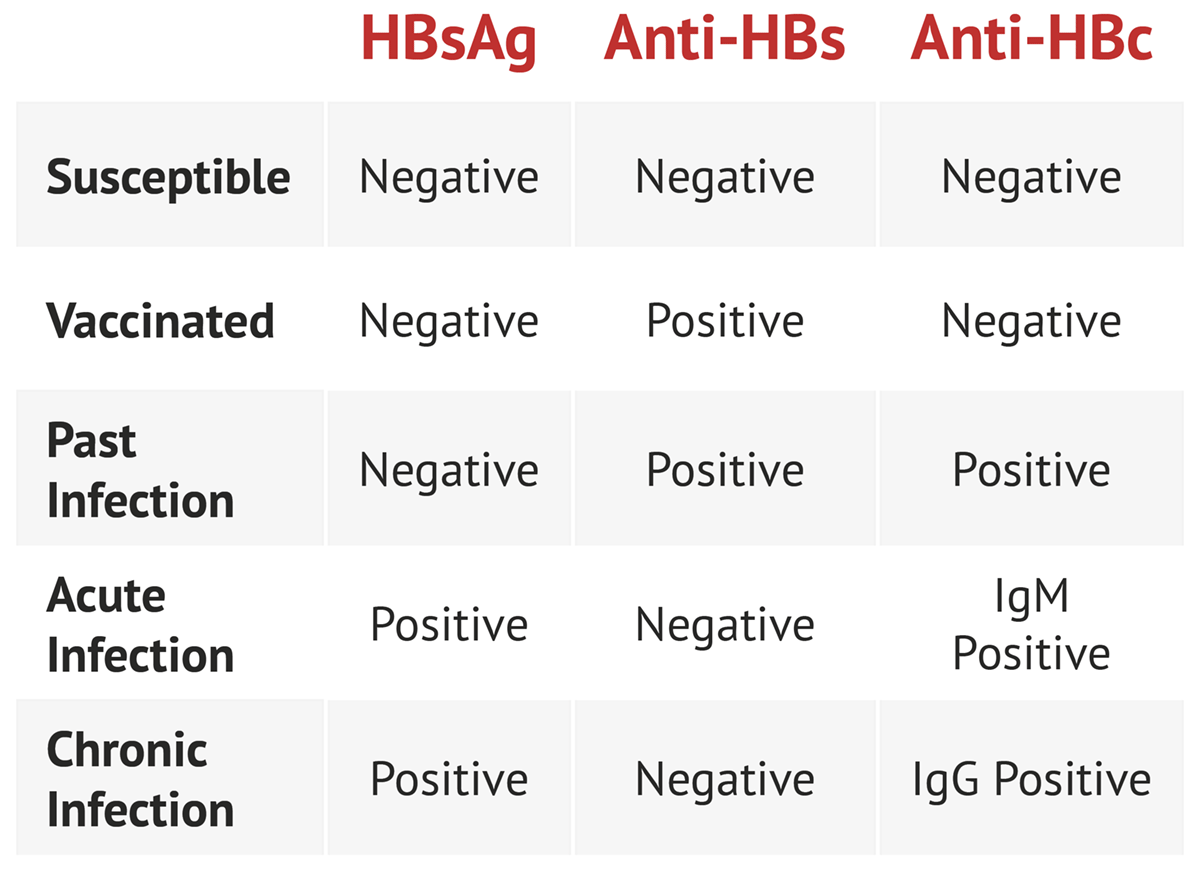
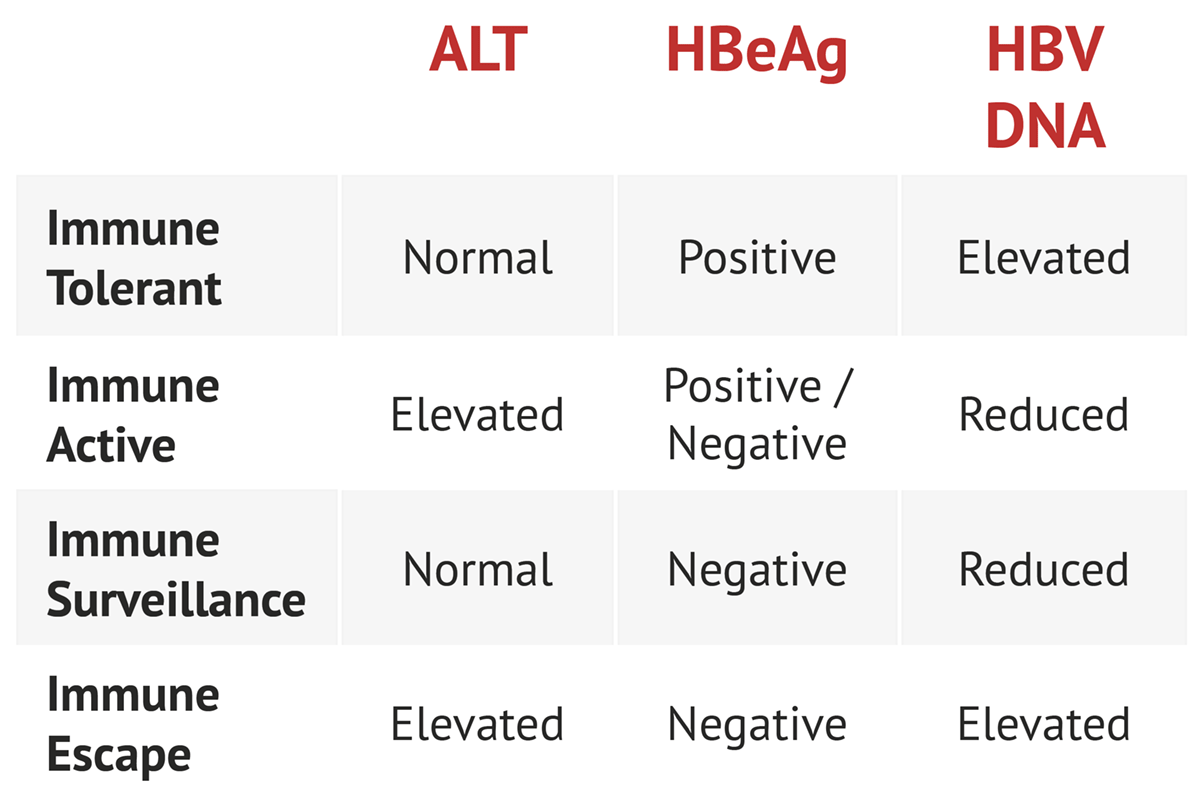
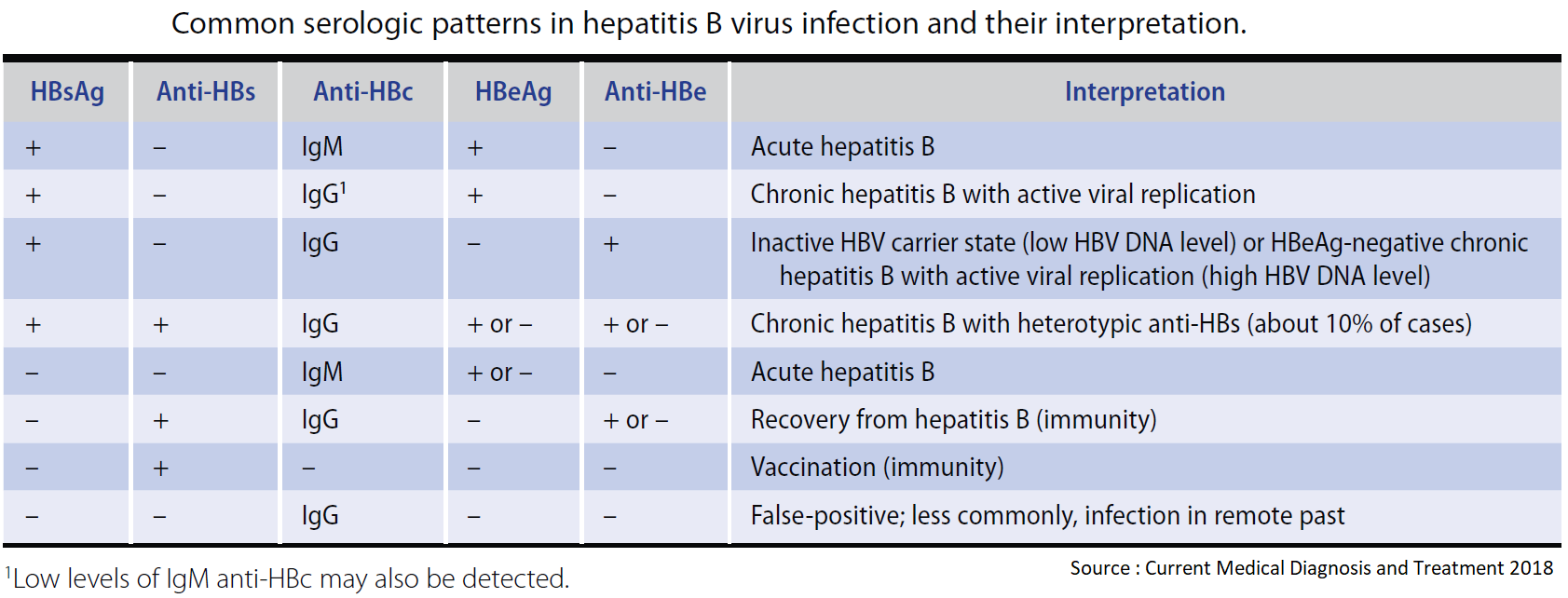
Bzowej8 and John B. Appendix 3 Hepatitis B Serology Results and Interpretation Diagnosis of HBV infection is usually through serological and virological markers. The definition and clinical use of common HBV serological markers are shown in Table 2.
People from endemic areas Asia Africa or injection drug users and those with high-risk sexual behaviours are at an increased risk for infection. Anti-HAV IgM IgM antibody to hepatitis A. HBsAg is the hallmark of HBV infection and is the first serological marker to appear in acute hepatitis B.
The incubation period of HBV infection ranges from 4 to 12 weeks and has a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations. Testing for Hepatitis A serology may be indicated for the work-up of patients with suspected acute viral hepatitis to determine immune status following recovery from natural infection or as a result of immunization and as part of an epidemiologic investigation eg. Hepatitis B can be a complicated liver infection to understand so additional blood tests may be ordered so your doctor has a better understanding of what kind of care and follow-up is needed.
Specimen Collection and Handling. IgM anti-HAV is usually present 5-10 days before symptom onset and declines to undetectable levels within six months of initial infection. Persistence of hepatitis B surface antigen for more than 6 months after an acute infection is by definition chronic hepatitis B3 Furthermore his Hepatitis B e antigen is positive indicating high infectivity.
Hepatitis B virus HBV chronically infects approximately 250000 Canadians and 350 million. Hassan Murad6 See Editorial on Page 31 Objectives and Guiding Principles. 7 rows Interpreting hepatitis B serological test results.
Hepatitis B surface antigen begins to rise just before 4 weeks after exposure peaking at less than 12 weeks after which it falls to zero at 24 weeks. Bzowej2 Kyong-Mi Chang3 Jessica P. AASLD 2018 Hepatitis B Guidance Norah A.
This training includes an animated video with voiceover that covers the serologic tests for acute and chronic hepatitis B virus HBV infection the serological diagnosis of HBV the meanings of serologic markers and interpret serologic test results. Hepatitis B e-antigen is present until just after the peak in hepatitis B surface antigen levels at 12 weeks. After this point hepatitis B e-antigen disappears and hepatitis B e-antibody appears.
This is a protein that is found on the surface of the hepatitis B virus molecule a part of the virus itself.