Arterial Insufficiency Vs Venous Insufficiency Chart
Occlusion of a large aortic branch including renal SMA or subclavian arteries with distal ischemia.
Arterial insufficiency vs venous insufficiency chart. Objective testing of venous function is considered reasonable and necessary in patients that are candidates for anticoagulation or invasive therapeutic procedures for any one of the following. Contraindications Aortic insufficiency Aortic dissection severe peripheral vascular disease Complications Leg ischemia. The most common complication.
Where medical services are less well developed the risk of dying from DKA is greater and children may die before receiving treatment. Diabetes symptoms type 1 vs type 2 pancreas. Evaluation of Postthrombotic Postphlebitic Syndrome PTS in.
The College of Surgeons of East Central and Southern Africa COSECSA is an independent body that fosters postgraduate education in surgery and provides surgical training throughout East Central and Southern Africa. As opposed to IPC. The point prevalence of open venous leg ulcers in the UK is about 3 cases per 10000 people and many people experience recurrent episodes of prolonged ulceration.
Before cutting out the figures on this page Vesalius suggests that readers glue the page onto parchment and gives instructions on how to assemble the pieces and paste. Firstline treatment for venous leg ulcers is compression therapy but a wide range. Pertinent findings should be documented in the patients chart.
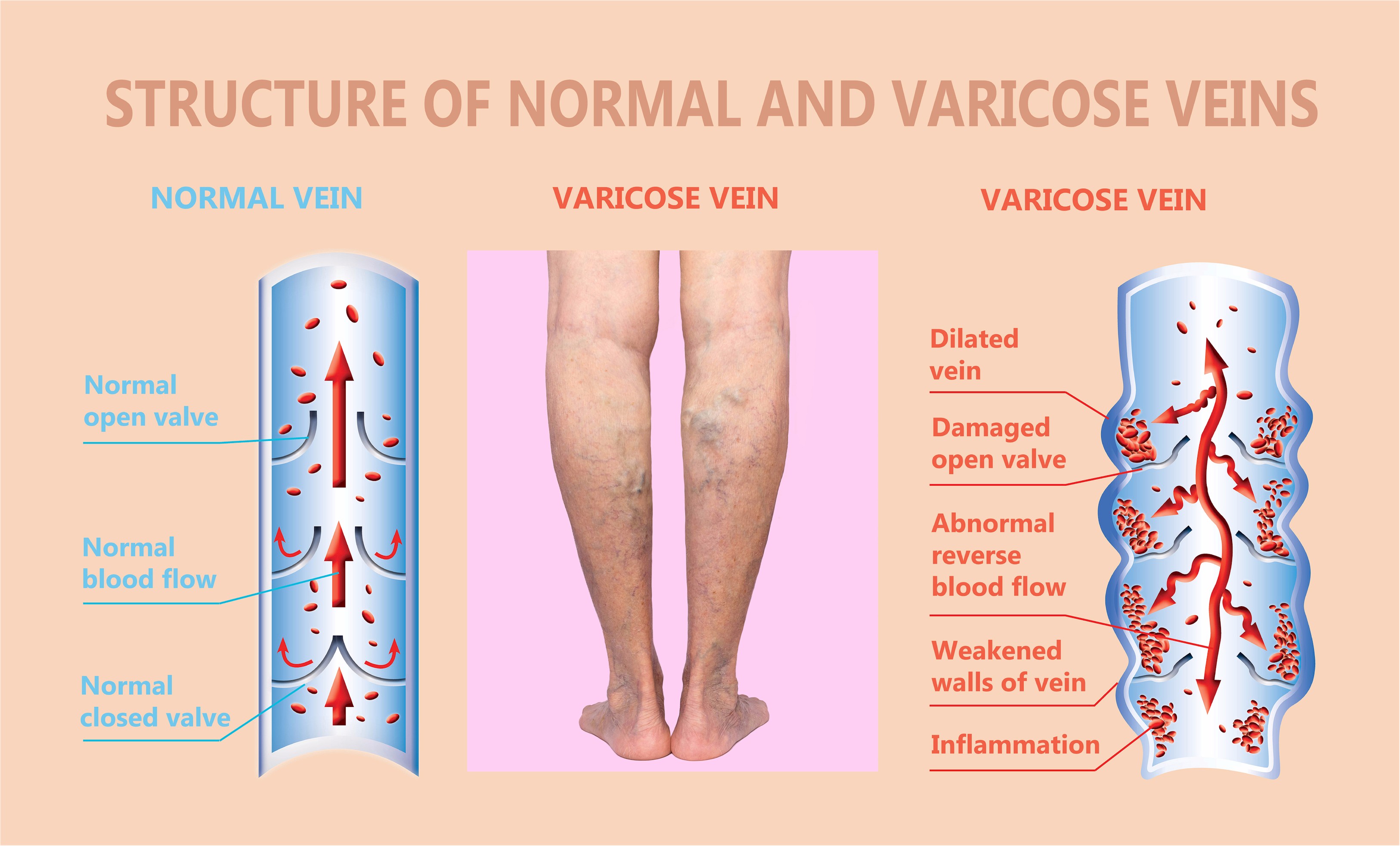
Inadequate expulsion of venous blood results in stasis and a persistently elevated venous pressure or venous hypertension. Acute aortic dissection or perforation. The management of stable fibroatheromatic plaque reduces the risk of ischemic diseases and its related deaths.
Venous valvular reflux in veins not involved at the time of acute deep vein thrombosis. Human anatomical chart of blood vessels with heart lungs liver and kidneys included. Meissner MH Manzo RA Bergelin RO Markel A Strandness DE Jr.
2013 ESHESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. The role of chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency CCSVI in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis MS is a matter of debate. In addition if patient had a prior procedure via femoral access review of any.
Chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency was first diagnosed using specialized trans-cranial and extra-cranial Doppler ultrasonography. Some have advocated the use of MRV in place of trans-cranial Doppler because the results of MRV are. Mechanical changes include thickening of arterial wall alteration of arterial elasticity contraction of smooth muscle increase in sensitivity to pharmacological stimulation and increase in arterial viscoelasticity ie arteriosclerosis.
Venous leg ulcers are open skin wounds on the lower leg which can be slow to heal and are both painful and costly. Daniel DeSalvo noted that many of the 42 Factors that affect blood sugar are truly amplified in the hospital. The predominant cause is maternal.
Hematoma at insertion site. Other organs are numbered and arranged around it. Presence of any of the above conditions should prompt strong consideration for an alternative approach such as radial preferred or brachial artery although these are not absolute contraindications for a femoral artery approach.
Overall cerebral edema accounts for 6090 of all DKA-related deaths in children. Venous insufficiency is the most common. Decreased venous compliance also results from an intrinsic myogenic increase in venous smooth muscle tone in response to the elevated pressure in the veins of the lower body.
Caps MT Manzo RA Bergelin RO Meissner MH Strandness DE Jr. In particular it has been shown that the use of GCS on legs with. Chronic venous insufficiency is impaired venous return which may cause lower extremity symptoms.
Even for experienced endocrinologists achieving tight blood sugars in the hospital can be very challenging especially for very sick patients on multiple medicationsIndeed Dr. 201202 Other contraindications for GCS comprise of arterial insufficiency and peripheral neuropathy due to potential skin damage. Together these mechanisms normally stabilize blood pressure within a.
Macrosomia is birthweight 4000 g in a term infant. The Fenton growth charts provide a more precise assessment of growth vs gestational age. The relationship between lysis and subsequent reflux.
Cerebral venous thrombosis CVT is an important cause of stroke in young adults mean age 33 years with a two-thirds female preponderance 1 caused by complete or partial occlusion of the cerebral major cerebral venous sinuses cerebral venous sinus thrombosis or the smaller feeding cortical veins cortical vein thrombosis. JACS has partnered with COSECSAs journal East and Central African Journal of Surgery to provide mentorship and promote friendship and the. The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension ESH and of the European Society of Cardiology ESC AuthorsTask Force Members AuthorsTask Force Members Search for other works by this author on.
With progression fibrosis compromises tissue oxygenation and ulceration may result. After venous insufficiency occurs no treatment is. As fibrin extravasates and inflammation occurs the superficial tissues become edematous and hyperpigmented.
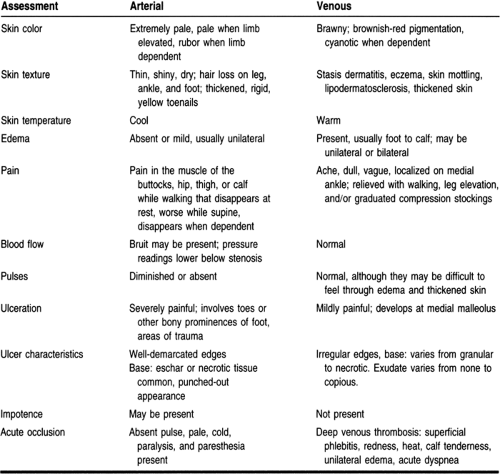
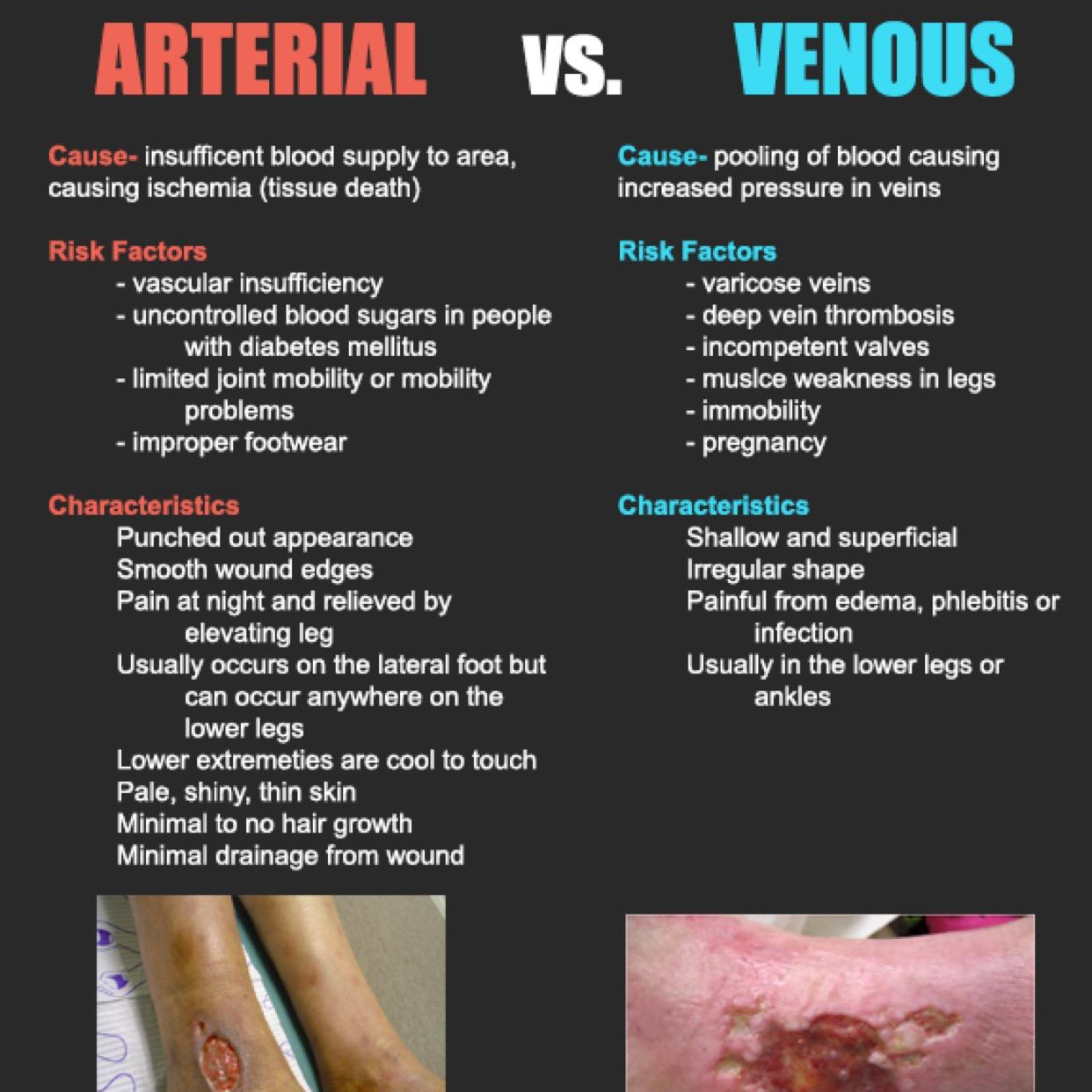
Acute peripheral arterial insufficiency Preparation and preservation of compromised skin grafts not for primary management of wounds Soft tissue radionecrosis as an adjunct to conventional treatment Tp02 used to determine a line of demarcation between viable and non-viable tissue when surgery or amputation is anticipated Limitations A routine history and. Describe the clinical manifestations the nurse would anticipate for venous insufficiency versus arterial insufficiency. Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolic Disease Version 22021 NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology Authors.
The relationship between lysis and subsequent reflux. Other compensatory mechanisms include the veno-arteriolar axon reflex the skeletal muscle pump and respiratory pump. There are separate charts for boys Fenton growth chart for preterm boys Infants whose weight is the 90th percentile for gestational age are classified as large for gestational age.
Distal pulses should be monitored at least hourly.