Amino Acid Code Chart
Structure of Amino Acids.
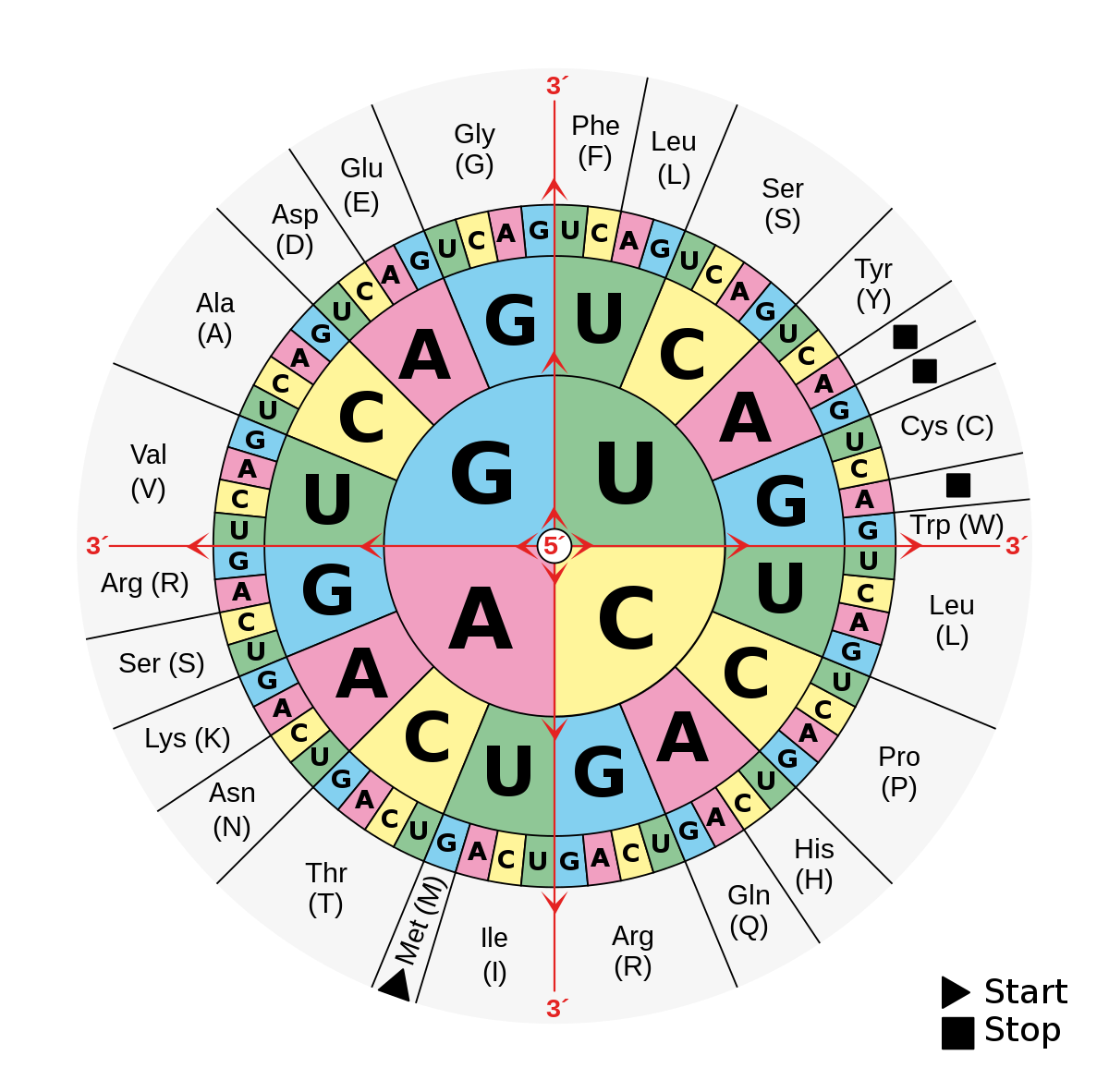
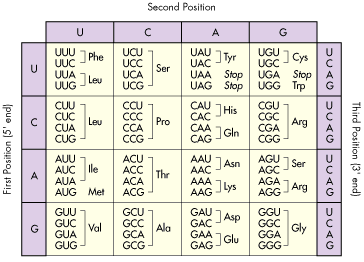
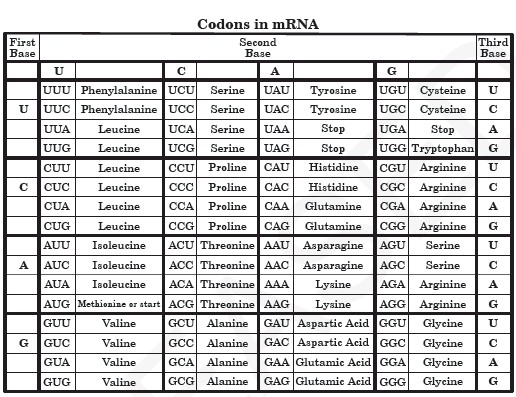
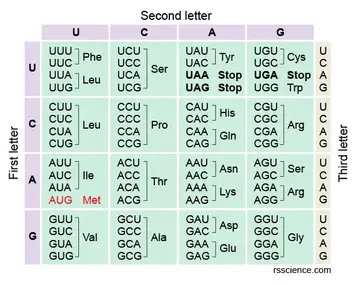
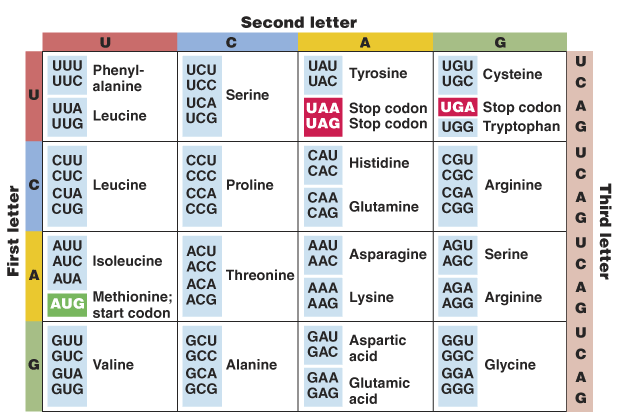
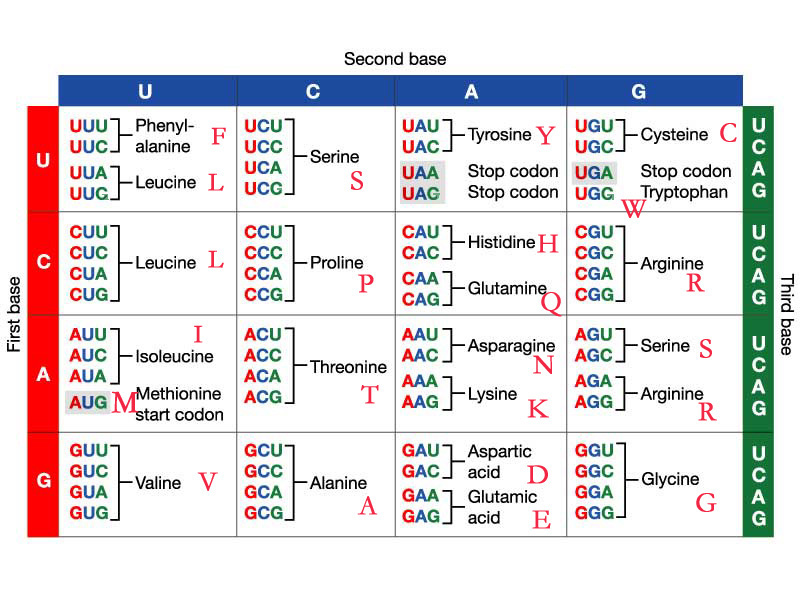
Amino acid code chart. CGT CGC CGA CGG AGA AGG. A codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. AUG coding for Methionine is the only codon that.
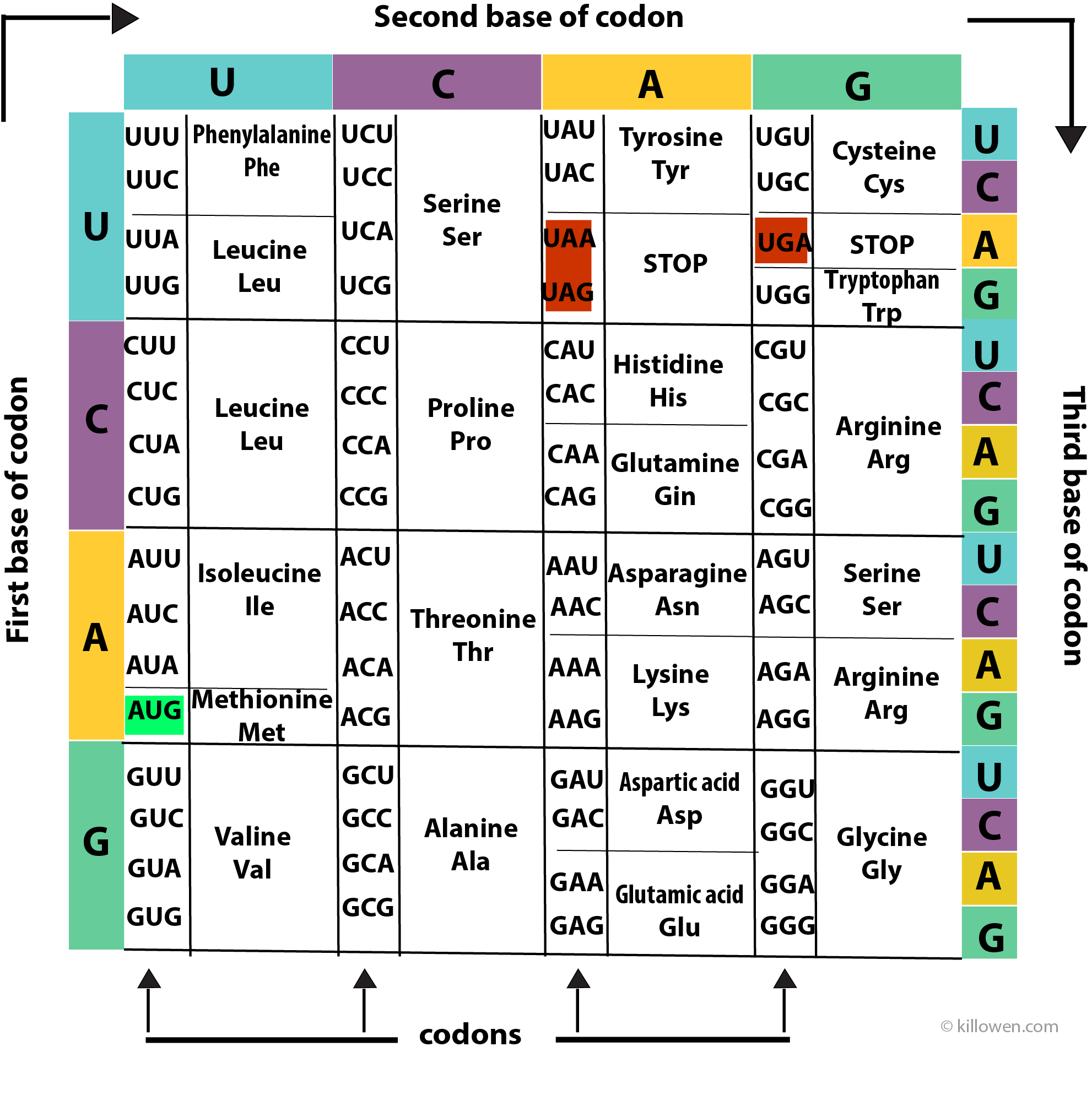
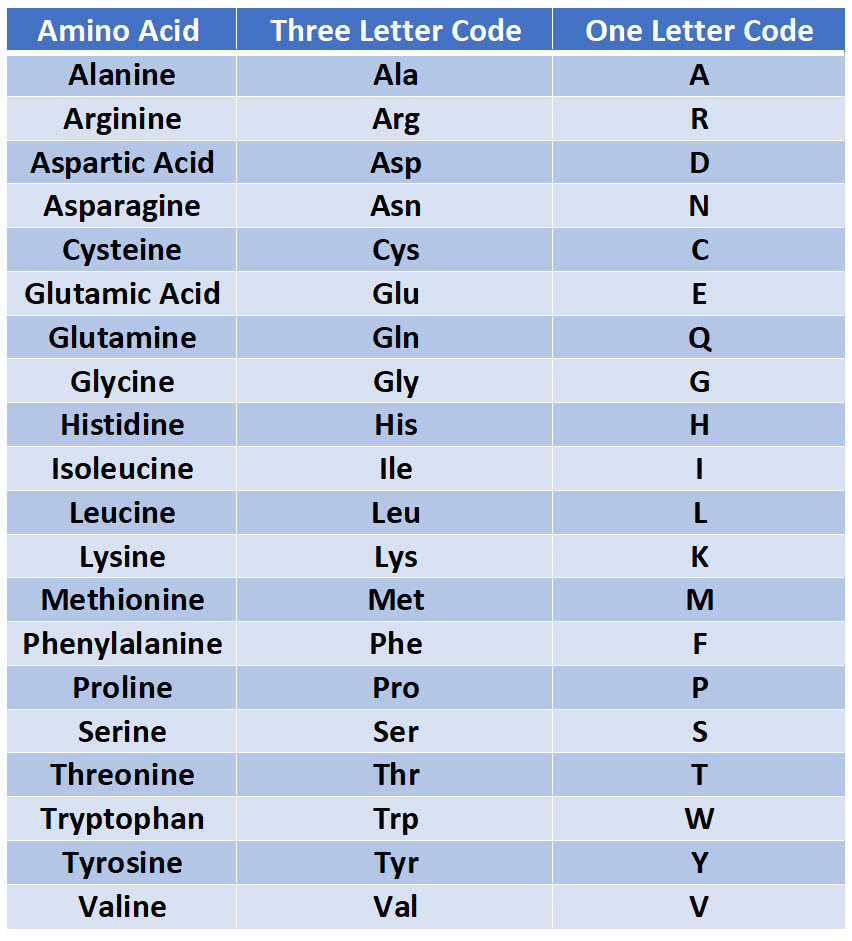
TAA TAG TGA In this table the twenty amino acids found in proteins are listed along with the single-letter code used to represent these amino acids in protein data bases. Amino acids are organic compounds containing amine - NH 2 carboxyl -COOH side chain R group The major key elements if amino acids are carbon hydrogen nitrogen oxygen. Glutamine or glutamic acid.
About 500 amino acids are known though only 20 appear in the genetic code and can be classified in many ways WHAT ARE AMINO ACIDS. Each codon codes only for one specific amino acid. Approximately 500 of them exist but only 20 appear in our genetic code.
Use the following as a reference guide for amino acid names abbreviations and structures. In doublet- 2 nucleotide code per amino acid it can able to make only 16 possible combinations for 20 different amino acids. May it be a hormone an enzyme a structural protein like keratin all of these are made up of amino acids.
CGU would code for Arginine in animals as well as in bacteria but exceptions exist. The full set of relationships between codons and amino acids. Genetic-Code-Amino-Acid-Codon-Chartpdf 1 4819 115 PM.
Those shown below are known as standard amino acids. Selenocysteine is often referred to as the 21st amino acid but is encoded in a special manner. The 64 possible triplets and the amino acids they specify are called the genetic code or.
In this context the standard. 22 rows The amino acids codon chart. The DNA codons representing each amino acid are also listed.
Amino Acids Reference Guide Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Amino acid reference chart contains the twenty amino acids found in eukaryotes grouped. The general structure of Amino acids is H2NCH RCOOH and it can be written as.
A ALA d-ALA Arginine. Out of 64 codons 3 are stop codons which do not code for any amino acids and thus ends the process of translation. Amino acids polymerize to produce proteins.
Therefore the triplet codon theory suite more appropriately for the genetic code. And as we know that codes cant overlap doublet codon theory cant be possible to code for all 20 amino acids. This chart only shows those amino acids for which the human genetic code directly codes for.
There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids and all have common structural features an amino group -NH3 a carboxylate -COO- group and a hydrogen-bonded to the same carbon atom. The mRNA sequence is determined by the sequence of genomic DNA. Since every amino acid has a basic NH2 end and an acidic COOH end these terminals react with each other making a chain of amino acids.
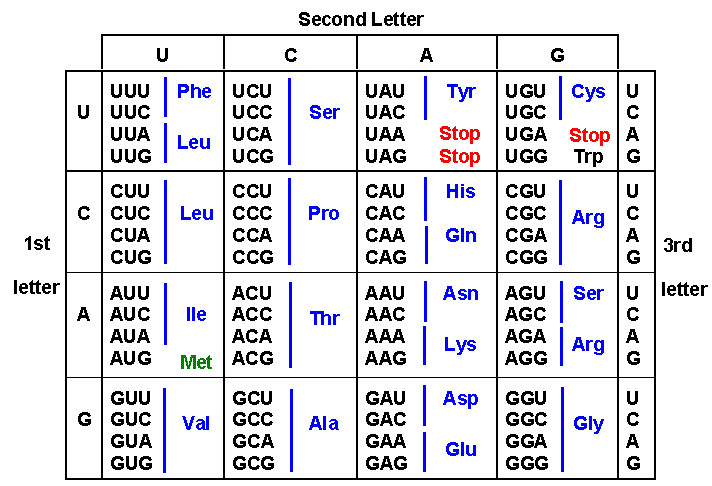
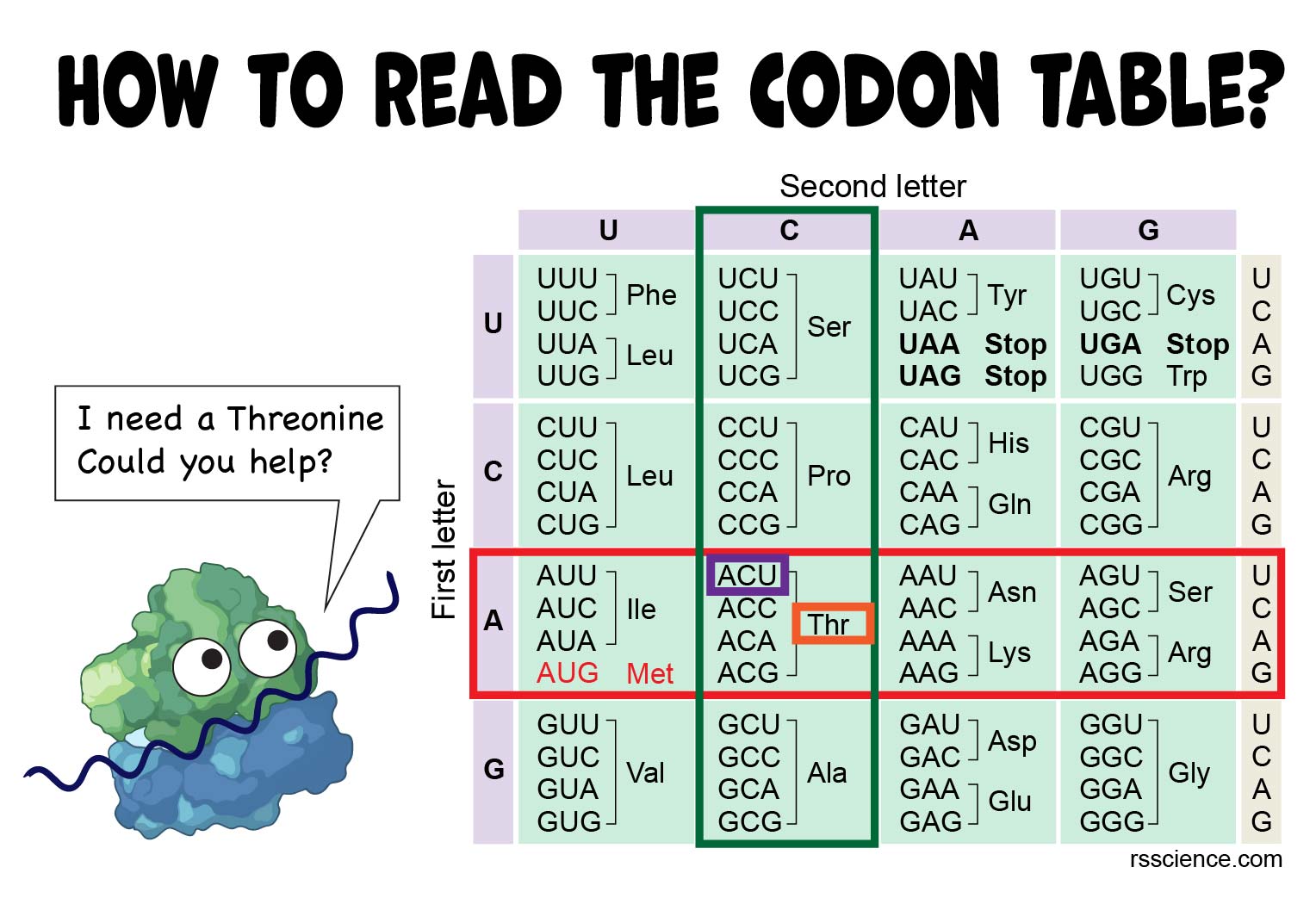
The simple 3 step directions indicate that you first need to select the nitrogenous base and then match it to the first letter on the table. 86 rows Single Letter Code Multiple Letter Code D-Amino Acid Code Alanine. The amino acid chart provided by Oregon State is a color-coded table that makes it possible to translate different parts of mRNA code into a sequence of amino acids.
Stop codons Stop. The codes are universal irrespective of the type of organism ie. Asparagine or aspartic acid.
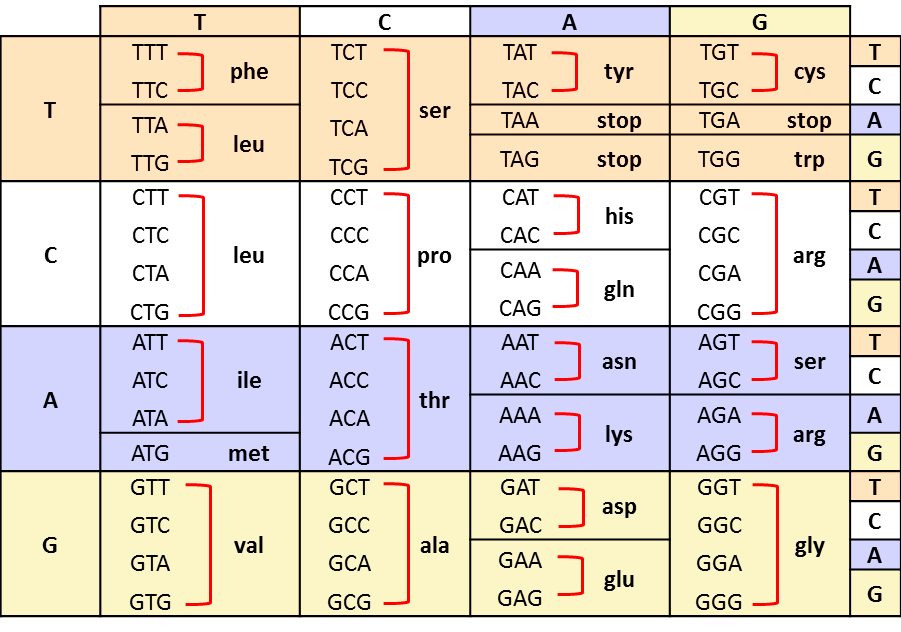
The standard genetic code is traditionally represented as an RNA codon table because when proteins are made in a cell by ribosomes it is messenger RNA that directs protein synthesis. Second Position First Position Third Position T C A G T C A G TTT TTC TTA TTG TCT TCC TCA TCG TAT TAC TAA TAG TGT TGC TGA TGG CTT CTC CTA CTG CCT CCC CCA CCG CAT CAC CAA CAG CGT CGC CGA CGG ATT ATC ATA ATG ACT ACC ACA ACG AAT AAC AAA AAG AGT AGC AGA AGG GTT. 26 rows code Three letter code Amino acid Possible codons.